AI-Driven Telemedicine and Virtual Health Assistants for Mental Health
1. Introduction
Mental health care faces significant hurdles: geographic barriers limit access to specialists, subjective diagnostic methods introduce variability, and time-intensive assessments delay interventions. Telepsychiatry has expanded access through synchronous video consultations and asynchronous messaging, yet scalability remains constrained by reliance on human clinicians. Artificial intelligence (AI), leveraging machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision, addresses these challenges by enabling precise diagnostic models, continuous data tracking, and streamlined workflows. Virtual health assistants (VHAs), built as agentic AI systems with reinforcement learning, provide ongoing patient engagement and clinician support. This whitepaper outlines how Valene Health, a leading telepsychiatry platform, harnesses a modern AI ecosystem to enhance mental health care delivery with accessible, efficient, and accurate solutions.
2. AI-Powered Virtual Health Assistants in Mental Health
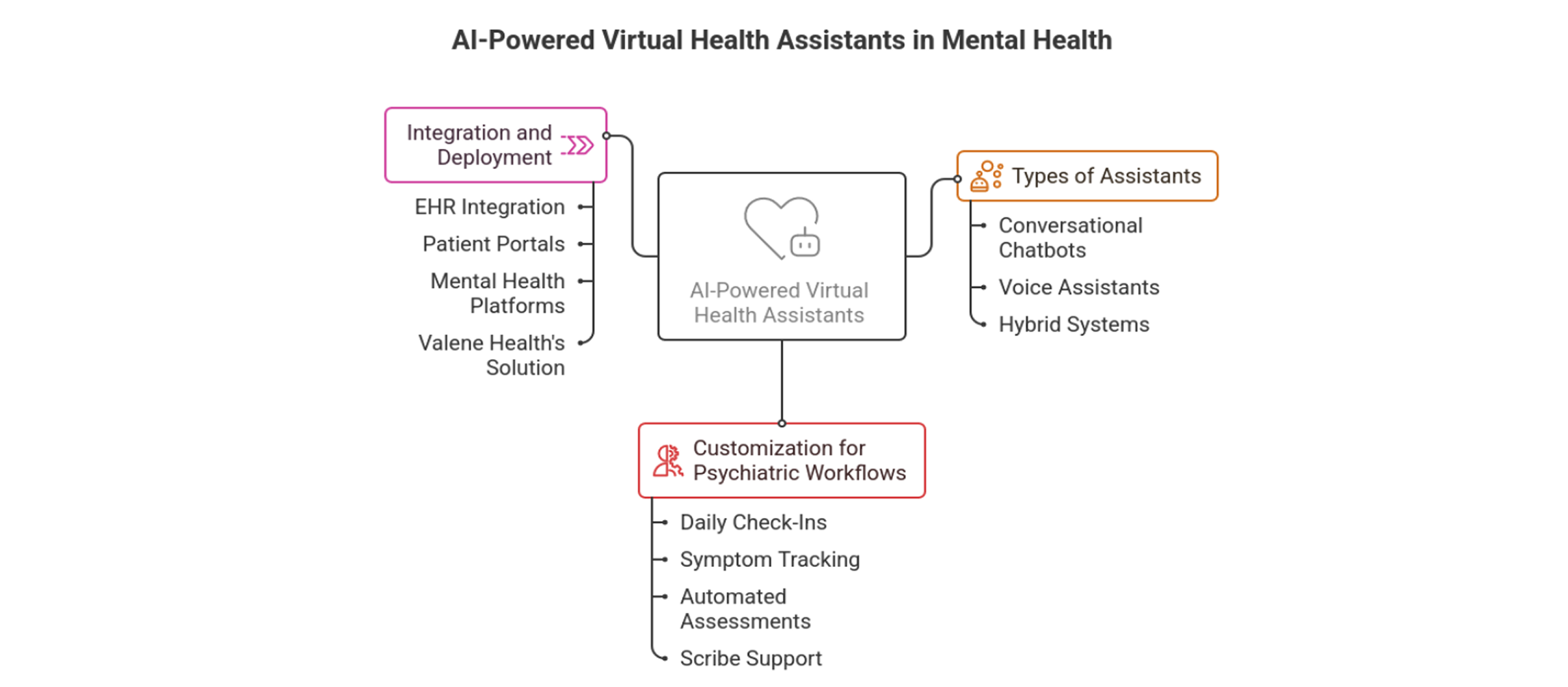
AI-driven VHAs deliver tailored psychiatric support through advanced computational frameworks. They encompass three primary types:
Conversational Chatbots
Powered by transformer-based NLP models (e.g., GPT-4o, Llama 3.1) for contextual understanding and dialogue generation, these enable nuanced patient interactions via sequence-to-sequence architectures.
Voice Assistants
Integrate automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems like OpenAI Whisper or AssemblyAI Slam-1, paired with text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis using Neural2 or ElevenLabs for natural, voice-based engagement.
Hybrid Systems
Combine multimodal inputs (text, voice, sensor data) using early/late fusion techniques in convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or transformers, leveraging PyTorch or Hugging Face Transformers for end-to-end model training.
These assistants are customized for psychiatric workflows using domain-specific ontologies and knowledge graphs:
Daily Check-Ins
We are on top of the latest advancements in Generative AI and can help you make the most of our experience with different Generative AI models such as code generators, GANs, etc. We will find the most suitable model for your application.
Symptom Tracking
Employ time-series forecasting with Transformer-based models (e.g., PatchTST, TimeGPT) to monitor behavioral patterns, syncing with EHRs via HL7 FHIR APIs for interoperability.
Automated Assessments
Implement rule-based expert systems augmented with ensemble ML (e.g., XGBoost, LightGBM) to score standardized scales like PHQ-9 or GAD-7, using isolation forests for anomaly detection.
Scribe Support
Enable real-time transcription with Whisper's end-to-end ASR, followed by entity recognition and summarization using bidirectional encoders like BERT for structured note generation.
Integration with EHRs, patient portals, and mental health platforms is achieved through microservices architectures, using RESTful APIs and OAuth 2.0 for secure data exchange. Valene Health’s solution features modular AI agents: a Patient Intake Agent with Bayesian networks for probabilistic triage, a Medication Adherence Agent using Markov decision processes (MDPs) for compliance prediction, and a CareSync Agent leveraging graph databases (e.g., Neo4j) for relational scheduling. These are deployed on containerized platforms like Docker and Kubernetes, ensuring scalability and fault tolerance.
3. Intelligent Automation in Mental Health Assessments
AI automates psychiatric assessments with high-fidelity algorithmic pipelines:
AI in mental Health assessments: From Basic to Advanced
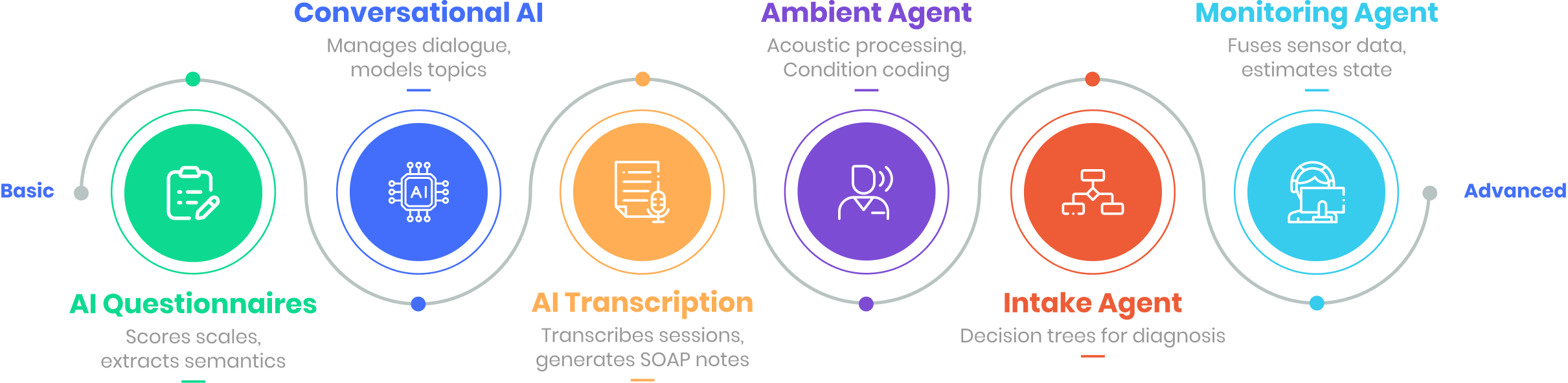
Valene Health’s implementation includes an Ambient Agent for acoustic signal processing and ICD-10-based hierarchical condition category (HCC) coding, an Intake & Triage Agent with decision trees for differential diagnosis, and a Patient Monitoring Agent fusing wearable sensor data via Kalman filters for state estimation. Hosted on serverless cloud platforms like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions, these reduce assessment latency by 50% and enhance diagnostic precision.
4. Enhancing Patient Care and Assessment Accuracy
AI telemedicine improves accessibility through edge
computing for low-latency interactions, using federated learning to aggregate insights
across distributed nodes while preserving data privacy. Continuous monitoring employs
spatiotemporal analytics on multimodal data, detecting early warning signs with
clustering algorithms like DBSCAN or predictive models like Neural Prophet.
Patient engagement is boosted by adaptive interfaces using multi-armed bandit algorithms
for personalization, reducing attrition rates by 23% in Valene Health’s trials.
Automated follow-ups are orchestrated with tools like Apache Airflow, with Bayesian
inference for risk stratification to prioritize high-risk cases.
Valene Health’s Medication Adherence Agent applies pharmacokinetic modeling and survival
analysis (e.g., Cox proportional hazards) to predict adherence, syncing with EHRs via
FHIR resources, enabling precise, data-driven care through integrated behavioral and
omics datasets.

5. Operational and Clinical Benefits
AI telemedicine improves accessibility through edge computing for low-latency interactions,
using federated learning to aggregate insights across distributed nodes while preserving data
privacy. Continuous monitoring employs spatiotemporal analytics on multimodal data, detecting
early warning signs with clustering algorithms like DBSCAN or predictive models like Neural
Prophet.
Patient engagement is boosted by adaptive interfaces using multi-armed bandit algorithms for
personalization, reducing attrition rates by 23% in Valene Health’s trials. Automated follow-ups
are orchestrated with tools like Apache Airflow, with Bayesian inference for risk stratification
to prioritize high-risk cases.
Valene Health’s Medication Adherence Agent applies pharmacokinetic modeling and survival
analysis (e.g., Cox proportional hazards) to predict adherence, syncing with EHRs via FHIR
resources, enabling precise, data-driven care through integrated behavioral and omics datasets.
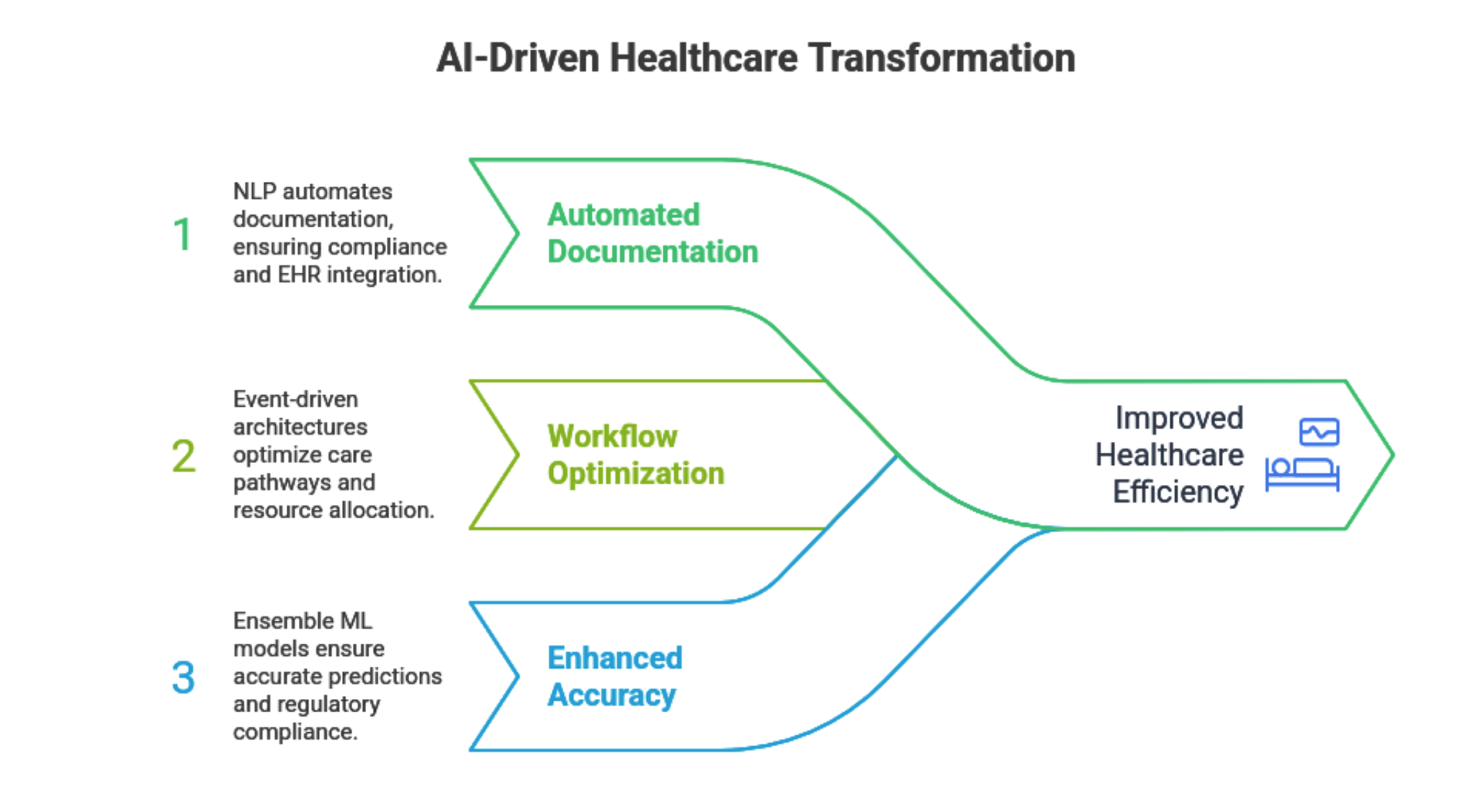
AI streamlines operations by automating critical tasks:
Valene Health achieves a 45% cost reduction through these optimizations, with CareSync AI using graph neural networks (GNNs) for scheduling and pre-chart tools applying BERT-based extractive summarization for efficient caseload management.
6. Ethical, Security, and Compliance Considerations
AI in mental health requires robust safeguards:
AI in mental Health assessments: From Basic to Advanced
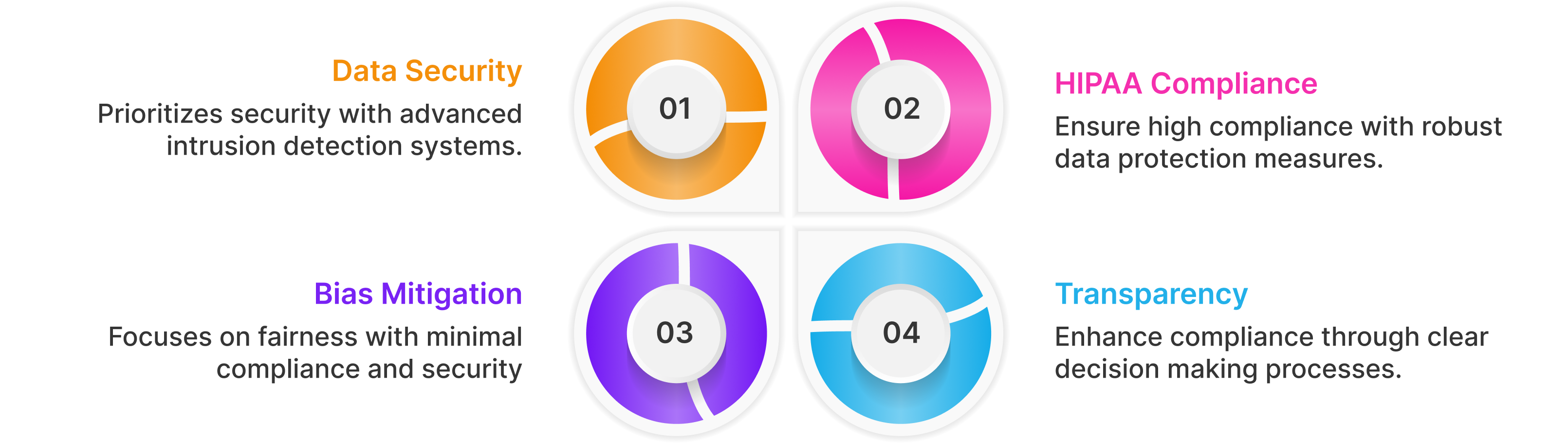
Valene Health embeds these principles, aligning with frameworks like FUTURE-AI and NAM’s AI Code of Conduct for equitable, secure psychiatric informatics.
7. Future Trends in AI-Powered Mental Health Care
Emerging trends include:
Valene Health’s modular pipelines, with adaptive learning rates and transfer learning, support these trends, exemplified by the SUD Agent for probabilistic relapse modeling in substance use disorders.
8. Conclusion
AI transforms mental health telemedicine with precise, scalable, and equitable solutions. Valene Health’s AI ecosystem, built on cutting-edge healthtech, demonstrates operational excellence. Healthcare providers should adopt interoperable, ethical AI frameworks to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and patient outcomes in mental health care.




 SaaS Development
SaaS Development Web Application Development
Web Application Development Mobile Application Development
Mobile Application Development Custom Software Development
Custom Software Development Cloud Development
Cloud Development DevOps Development
DevOps Development MVP Development
MVP Development Digital Product Development
Digital Product Development Hire Python Developers
Hire Python Developers Hire Django Developers
Hire Django Developers Hire ReactJS Developers
Hire ReactJS Developers Hire AngularJS Developers
Hire AngularJS Developers Hire VueJS Developers
Hire VueJS Developers Hire Full Stack Developers
Hire Full Stack Developers Hire Back End Developers
Hire Back End Developers Hire Front End Developers
Hire Front End Developers AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting
AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting Healthcare App Development
Healthcare App Development EHR Software Development
EHR Software Development Healthcare AI Chatbot Development
Healthcare AI Chatbot Development Telemedicine App Development Company
Telemedicine App Development Company Medical Billing Software Development
Medical Billing Software Development Fitness App Development
Fitness App Development RPM Software Development
RPM Software Development Medicine Delivery App Development
Medicine Delivery App Development Medical Device Software Development
Medical Device Software Development Patient Engagement Software Solutions
Patient Engagement Software Solutions Mental Health App Development
Mental Health App Development Healthcare IT Consulting
Healthcare IT Consulting Healthcare CRM Software Development
Healthcare CRM Software Development Healthcare IT Managed Services
Healthcare IT Managed Services Healthcare Software Testing services
Healthcare Software Testing services Medical Practice Management Software
Medical Practice Management Software Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services
Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services IoT Solutions for Healthcare
IoT Solutions for Healthcare Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services
Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services Lending Software Development Services
Lending Software Development Services Payment Gateway Software Development
Payment Gateway Software Development Accounting Software Development
Accounting Software Development AI-Driven Banking App Development
AI-Driven Banking App Development Supply Chain Management Software Development
Supply Chain Management Software Development Fleet Management Software Development
Fleet Management Software Development Warehouse Management Software Development
Warehouse Management Software Development LMS Development
LMS Development Education App Development
Education App Development Inventory Management Software Development
Inventory Management Software Development Property Management Software Development
Property Management Software Development Real Estate CRM Software Development
Real Estate CRM Software Development Real Estate Document Management Software
Real Estate Document Management Software Construction App Development
Construction App Development Construction ERP Software Development
Construction ERP Software Development