Power of Generative AI in Pharma: Accelerate Drug Discovery and Development
Contents
- Generative AI Opportunity in Biopharma
- Steps to Accelerating Drug Development and Approval
- The Remarkable Value of Document Automation
- Best Practices for Implementation and Change Management
- Conclusion: Charting the Future of AI-Driven Pharma Innovation
1. Generative AI Opportunity in Biopharma
The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the integration of Generative AI (GenAI). This advancement is revolutionizing various stages of AI drug discovery and development, from initial research to clinical trials and regulatory submissions. By leveraging Generative AI pharma solutions, pharmaceutical companies have accelerated the drug development process, reduced costs, and improved the accuracy and efficiency of regulatory documentation.
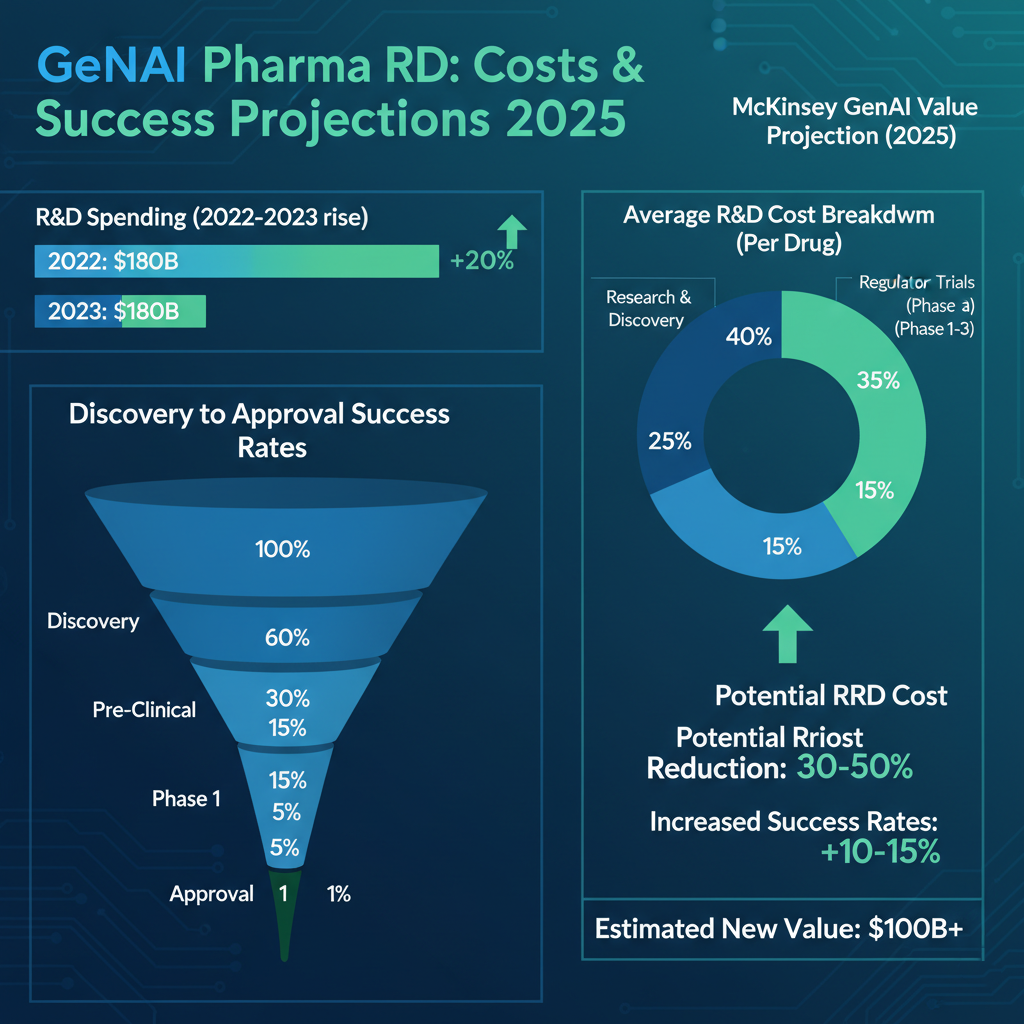
Spending on research and development (R&D) across drug discovery, development, clinical testing, and safety monitoring has significantly increased over time. According to a Deloitte study of the top 20 biopharma companies, total reported R&D spending rose by 4.5%, from $139.2 billion in 2022 to $145.5 billion in 2023. In the future, regulatory uncertainty, supply chain concerns, labor shortages, and other complications will likely cause R&D costs to continue to rise. The drug development process is both costly and uncertain, with zero guarantee that a drug will reach the market. On average, it takes 12 years to discover and develop a new drug, costing between $1 billion and $2 billion. Throughout this process, only about 10% of candidate molecules progress to the clinical phase, and of those, only 10% are eventually approved, resulting in a 1% success rate from start to finish.
Efforts to reduce time and costs in drug development had largely limited success until the rapid release of COVID-19 vaccines. From the public identification of the virus to the first emergency use authorization in December 2020, it took Pfizer and BioNTech 11 months to reach the market. As this specific case demonstrates and drug discovery costs continue to rise, there is a significant opportunity for GenAI to expedite process development and reduce expenses.
The McKinsey Global Institute (MGI) estimates that AI technology has the opportunity to generate $60 billion to $110 billion a year in economic value for the pharmaceutical and medical product industries. This value primarily comes from faster identification of new drug compounds, quicker development and approval processes, and enhanced marketing efforts. In clinical development, which accounts for the bulk of costs, generative AI in drug discovery can reduce expenses by up to 50% by streamlining clinical trial processes and automating trial document drafting. Additionally, it has the potential to shorten trial timelines by over 12 months.
"In terms of the preclinical, GenAI has a lot of applicability to save resources. You can use GenAI to make predictions, from selecting targets for drug development, to putting together combinations of genes for prognosis. Once GenAI is optimized, it's going to reduce timelines by 50%."
– Former Clinical Development Director, Medical & Scientific Affairs at Biotech
Using generative AI in biopharma is a hot topic in the pharmaceutical industry, with speed and cost savings seen as potential benefits. The emergence of generative AI (GenAI) has the potential to reform early-stage drug discovery and development. Large language models are being harnessed to create novel molecules tailored for specific properties through Generative AI for molecule generation, positioning them as potential drug candidates while also revolutionizing various aspects of the drug development process.
This innovative methodology promises to potentially mitigate formidable costs and time constraints traditionally associated with drug discovery. It could also unveil previously overlooked therapeutic possibilities. To achieve these benefits, though, pharmaceutical company leaders need to make sure they have a sound strategy to implement and support the technology, as well as to manage the massive organizational change it will involve.
Biopharmaceutical companies have strong interest in using GenAI in drug discovery as costs rise and digital transformation is needed to remain competitive. GenAI has the potential to speed drug discovery and reduce the costs of finding new therapies, but implementation will vary based on many factors. EY-Parthenon teams have executed multiple digital transformation engagements with pharmaceutical organizations and have experience implementing GenAI into the drug discovery process.
In 2025, the GenAI in drug discovery market is valued at $318.55 million, projected to reach $2.85 billion by 2034 at a 27.42% CAGR, driven by AI's role in target identification and molecule generation. Broader AI in drug discovery and development applications are expected to hit $6.93 billion in 2025.
2. Steps to Accelerating Drug Development and Approval
On average, it takes a decade for a new medication to reach the market, prompting firms to find ways to accelerate the process safely. We have identified four workflows where AI can significantly reduce time, resources, and costs throughout the clinical trial process.
Interactive and Dynamic Study Design
Current Challenge: When defining study features, ambitious protocols can lead to extensive back-and-forth with sites such as hospitals or labs, which can operationalize the study. Considering potential changes in site capabilities or patient recruitment, and updates of site contracts and patient consent, the demographics might lead to many protocol review difficulties or errors.
AI Solution:Implementing AI early in study design can streamline execution, data collection, and analysis as well as downstream document authoring. AI algorithms can analyze historical data and current site performance metrics with predictive analytics in pharma to predict the best sites for patient recruitment and study success. This approach minimizes delays by matching trial needs with sites that have the right patients.
Software examples: Neurocor, Faro, Castor.

Targeted Patient Finding, Personalized Hiring, & Consent
Current Challenge: Finding suitable patients who meet specific criteria for a study can be slow and inefficient, leading to delays, increased costs, and sometimes study termination. Part of this process involves obtaining a research participant's signature on a consent form and providing adequate information to allow for an informed decision about participation in the clinical investigation (informed consent). Complex studies can take anywhere from 6 to 12 months, with up to a 30% dropout rate due to poor recruitment.
AI Solution: AI can identify eligible participants by analyzing diverse datasets, including electronic health records and genetic databases, through AI for patient recruitment in trials. It can then tailor informed consent forms (ICFs) to individual comprehension levels and health profiles, enhancing understanding and maintaining transparency. This process not only expedites recruitment but also improves the quality of participant engagement.
Software examples: Medidata, Veeva, Oracle Health.
Realtime Clinical Trial Monitoring and Optimization
Current Challenge: Monitoring clinical trials in real time can be challenging due to the sheer volume of data, manual interpretations, and the complexity of managing multiple trial sites simultaneously. This often leads to issues with data integrity, protocol adherence, and delayed responses to adverse events or anomalies.
AI Solution: AI can monitor vast streams of trial data in real time to provide immediate insights and alerts when deviations occur. This enables faster decision-making, better compliance with regulatory standards, and more efficient resource allocation. AI-driven monitoring can reduce trial durations, improve outcomes through precise and timely interventions, and accelerate trial document production.
Software examples: Antidote, Saama, Medidata Rave.
Auto Generation of Document First Drafts
Current Challenge: Generating first drafts and subsequent updates for clinical documentation, such as study reports and regulatory submissions, is time-consuming and prone to human error. Keeping these documents updated with the latest data and ensuring consistency across updates poses a significant challenge.
AI Solution: Generative AI automates the drafting and updating of complex regulatory and submission documents, ensuring they are generated quickly and accurately. By using predefined templates and current data inputs, AI can maintain document accuracy and consistency, significantly reducing the administrative burden on researchers and speeding up the regulatory submission process.
Software examples: Yseop Copilot.

3. The Remarkable Value of Document Automation
A recent report by Boston Consulting Group estimates that Generative AI in BioPharma can boost productivity by ~30% in certain functions. Three out of the top five most significant use cases imply document and content generation.
Regulatory document writing is highly complex because of evolving requirements across countries, including standards related to CTD, ICH, Transcelerate, and CDISC. Processes demand extensive collaboration across clinical, regulatory, quality, and safety departments, as well as with external partners, all working with multiple, often unstructured and non-standardized data sources. Many organizations still rely on manual processes and outdated systems, leading to intensive authoring and review cycles that can cause delays.
"Document authoring and management account for between 10 to 20% of drug development costs. GenAI can achieve up to 50% efficiency gains, dramatically accelerating the time it takes for a drug to get to market. These undeniable benefits account for why 80% of tier-1 life sciences companies are actively exploring automation."
– Emmanuel Walckenaer, CEO of Yseop
Preclinical
Throughout the Preclinical process, before therapies are introduced to humans, thousands of small reports are written at the end of each study. These reports are frequently rewritten when preparing AI in IND & NDA regulatory submissions to meet regulatory expectations and prevent future questions or refusal from health authorities. Introducing content automation technology during the review process of these documents can improve efficiency by 30-50%.
Clinical
The Clinical document landscape is vast and includes a variety of reports such as Clinical Study Reports (CSR), Patient Narratives, and Clinical Summaries. There is an opportunity to streamline content generation and collaboration across different groups to handle large volumes of documents more efficiently. GenAI can automate the writing of patient narratives, reducing the average writing time by 4 hours for each of the thousands of narratives generated annually. GenAI enables CSR writing to start earlier with first clinical data and be updated in clicks with final data, simplifying reviews and enabling parallelisation of summary writing, cutting weeks from last patient visit to submission.
Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Control (CMC)
In Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Control (CMC), data is collected from various plants and equipments, which is then reconciled to produce clean tables with the appropriate level of detail. Since much of the content is reused across different documents, GenAI is able to continuously enrich and update this information several times a year, supporting production acceleration and batch multiplication. Beyond drug approval, AI can help maintain and enrich these documents for decades.
Pharmacovigilance
In Pharmacovigilance, multiple data sources coexist, including unstructured data from patients and hospitals, with new safety case channels such as social media. By integrating GenAI with legacy software and database tools, pharmaceutical companies can effectively monitor patient side effects once drugs are on the market.
IND and NDA Submissions

Document automation expedites the initial IND submission to start the first clinical trial, enables continuous IND updates for additional trials, and facilitates the final NDA submission for new drug approval. These documents play a crucial role in bringing new drugs to market, reducing the time needed to introduce life-changing therapies, vaccines, and medicines. Generative AI streamlines document authoring by generating 80% of accurate initial drafts, freeing up writers from tedious and error-prone tasks. Implementing AI for document automation will augment the current document and submission workflows to:
- Manage templates and guidelines to generate ready-to-use drafts that auto-generate different content types (e.g., tables, figures, text) based on various structured and unstructured sources
- Manage multi-user collaboration, document lifecycle, and source updates
- Support document finalization and quality control (e.g., checks on data integrity, styling and formatting, hyperlinks, reference, and acronyms management) and content publishing for each region or country of submission
- Offer a smooth and seamless user experience and bridge the gap between data sources and end-users’ writing tools
- Support data and document industry standardization to maximize AI impact
"Each day that a new drug or vaccine gets to market sooner, it creates $1-3 million in accelerated revenue."
– Tim Coleman, CIO of Medicine Development, Lilly
4. Best Practices for Implementation and Change Management
Over the last 18 months, companies have made GenAI roadmaps a top strategic priority. To get started, pharmaceutical firms develop proof of concepts and prototypes to identify use cases with business potential. Before moving to implementation, leaders need to address certain success metrics, like whether the organization can implement at scale. While many firms are turning use cases into real-world applications, challenges remain.
Data Readiness
To implement at scale, GenAI must be tested using the company's data. This can cause hesitation for pharma manufacturers due to the associated risks. Companies can be reluctant to share data with partners, and for good reason. A fundamental challenge facing healthcare and pharma companies is storing and securing patient and clinical study data safely. Without access to the company's data during GenAI implementation, third-party vendors cannot test and validate that the solution provides the right results and value for users. Beyond access, data readiness for pharma AI projects is critical as data is not always available in a machine-readable format. In pharma, data is highly heterogeneous across studies, therapeutic areas, and companies. While guidelines for standardized clinical data have been available for several years, implementation projects are still ongoing. Managing different study designs and data structures requires additional steps during implementation and production.
Security & Technical Validation
To share data in a regulated environment, IT usually requires software to be GxP compliant and deployed in a secured environment. Pharma companies should work with GenAI companies that offer a parallelized workstream for IT validation through Security and validation in AI pharma processes. This approach allows the team to perform functional implementation alongside IT, ensuring the system is validated when it goes into production.
User Trust and Adoption
For full adoption, users must recognize the value of the technology and be willing to embrace it. Medical writers and other end users of GenAI technologies must trust that the tool will replicate their writing style and provide a reliable, secure, and comprehensive first draft. Organizations must address the impact of technology and the fear of the unknown.
"2023 was the year of POCs and 2024 will be the year of production."
– Dan Sheeran, AWS General Manager for Life Sciences
Fostering Trust and Adoption
To ensure your organization is prepared to adopt AI-driven pharma solutions for medical writing, begin by standardizing data sources, harmonizing pre-existing document templates and structures, and adhering to lean writing guidelines. Other ways to seamlessly integrate AI into medical documentation workflows include:
- Establish clear success criteria with users like the percentage of document coverage.
- Define how medical writers will use AI in end-to-end workflows. Address how writers will apply the company's styling guidelines and the impact on the review and validation process.
- Integrate AI as much as possible into the end-to-end workflow and existing tooling environment (e.g., Veeva and MS Word).
- Ensure that content generation matches the required style. If the formatting is not right, medical writers are unlikely to read the content. GenAI technology must produce polished, formatted documents to ease adoption and accelerate value realization.
- Provide user interfaces that offer trust and control over AI-generated results. This helps users understand how and why the texts were generated and the level of accuracy.
- Implement a 'Change Management' stream that focuses not only on training but also on a Business Process Analysis phase. From the beginning, communicate to users that there will be changes in workflows and that AI is meant to improve the existing workflow, not replicate it.
For AI to be successful at scale, organizations must analyze each step of the value chain, addressing current processes, structures, and more. The key is to ensure that employees understand the value the technology will bring, implement it effectively and efficiently, and scale it to transform existing processes.

Case Studies: Real-World 2025 Impacts
Insilico Medicine: AI-Designed Fibrosis Drug Advances to Phase II
Insilico Medicine's Pharma.AI platform, integrating PandaOmics for target discovery and Chemistry42 for molecule generation, delivered ISM001-055, a TNIK inhibitor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Discovered in 18 months at $2.6 million versus traditional 4 years, and $100 million positive Phase IIa results in Q1 2025 showed 25% lung function improvement in 120 patients, with 80% fewer adverse events than standards. A November 2025 collaboration with Eli Lilly, valued at over $100 million, applies to pharma. AI to Lilly's undisclosed targets, projecting 50% faster candidate optimization. Rentosertib, Insilico's first AI-designed drug, received USAN naming in March 2025, marking a milestone for AI in precision medicine and AI-driven pharmaceutical innovation.
Exscientia: Precision Oncology via Merged AI Platforms
Following its 2025 merger with Recursion Pharmaceuticals, Exscientia's Centaur Chemist platform fused with Recursion's phenomics screening, advancing six AI-generated molecules to Phase I by mid-2025. In a Bristol Myers Squibb partnership, EXS-21546 (immuno-oncology) achieved 70% tumor reduction in preclinical models, cutting design time by 75% and costs by 60%. The merger enabled end-to-end automation, reducing lead optimization from 12 to 4 months, with 2025 projections for two Phase II entries in rare cancers.
Roche: AI-Enhanced Brain Barrier Penetration
Roche's 2025 $55 million partnership with Manifold Bio utilized AI to design "shuttles" crossing the blood-brain barrier, targeting Alzheimer's. Manifold's platform screened 10,000+ pathways, identifying three candidates with 90% delivery efficacy in rodent models—versus 40% traditional—accelerating preclinical timelines by 50%. Integrated with Roche's ML models, this yielded 85% improved prediction accuracy for CNS drugs, per Q3 2025 data, supporting two IND filings.
PharmBERT: LLM for Drug Label Extraction
Developed in 2025, PharmBERT—a BERT-based LLM pre-trained on 138,924 DailyMed labels—outperformed BioBERT by 25% in ADR detection and ADME classification, automating 80% of pharmacokinetic extractions for 50+ submissions, saving 6 months per NDA.
5. Conclusion: Charting the Future of AI-Driven Pharma Innovation
The integration of Generative AI in the pharmaceutical industry has immense potential to revolutionize drug discovery, development, and approval. By automating tedious tasks, accelerating timelines, and reducing costs, GenAI can transform how therapies and medicines are brought to market. However, to harness the full potential of GenAI, organizations must carefully evaluate their data readiness, ensure robust security and technical validation, and foster user trust and adoption through clear communication and effective change management strategies.
The journey towards successful AI implementation requires understanding the value it brings, meticulous planning, and a commitment to scale the technology across the value chain. As companies continue to innovate and embrace GenAI, they will be better positioned to deliver life-saving therapies and medical advancements to patients more efficiently and effectively.
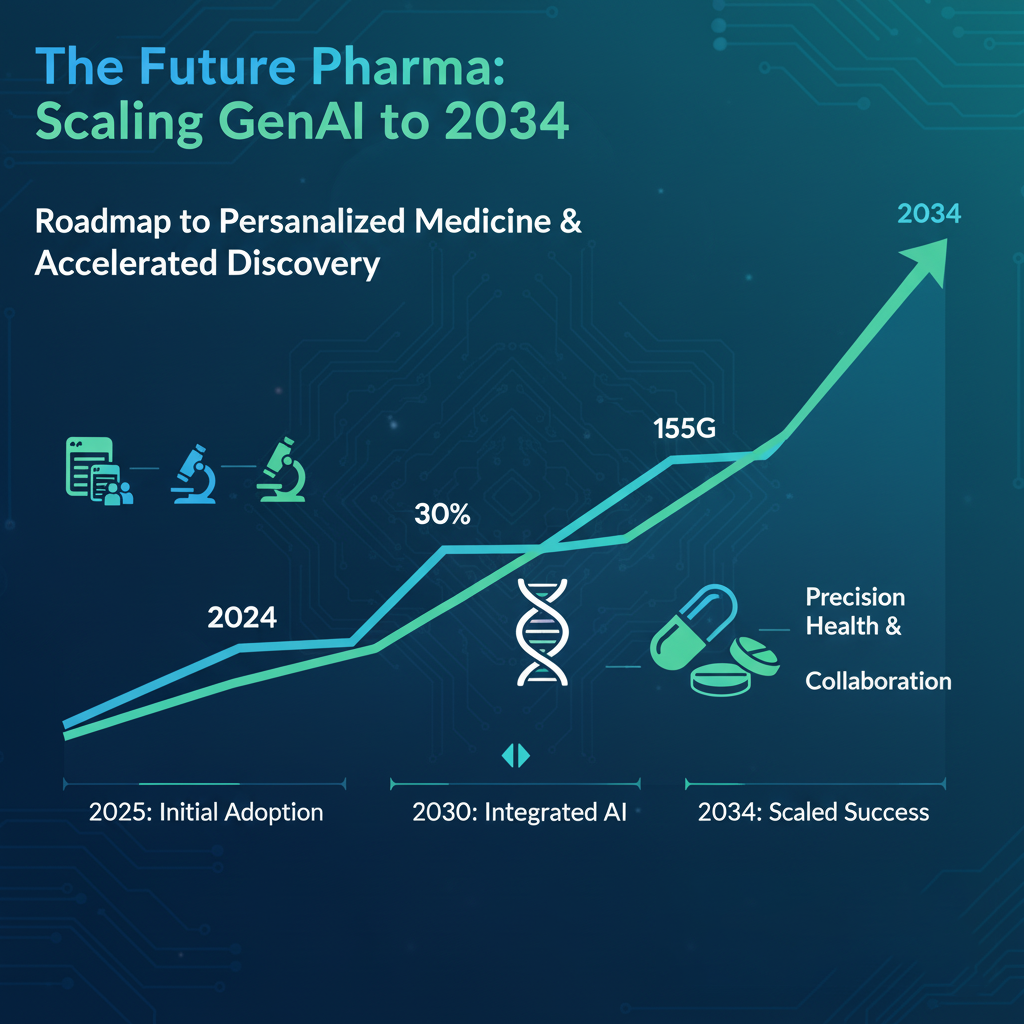
Looking to 2026 and beyond, GenAI will dominate 75% of pipelines, enabling precision therapies via multimodal models and hybrid AI-human workflows. With market growth at 27.42% CAGR, investments in platforms like Insilico's Pharma.AI signal a $16.5B AI pharma sector by 2034. Pharma leaders must prioritize ethical scaling to realize $60-110B annual value, turning challenges into opportunities for global health impact.






 SaaS Development
SaaS Development Web Application Development
Web Application Development Mobile Application Development
Mobile Application Development Custom Software Development
Custom Software Development Cloud Development
Cloud Development DevOps Development
DevOps Development MVP Development
MVP Development Digital Product Development
Digital Product Development Hire Chatbot Developers
Hire Chatbot Developers Hire Python Developers
Hire Python Developers Hire Django Developers
Hire Django Developers Hire ReactJS Developers
Hire ReactJS Developers Hire AngularJS Developers
Hire AngularJS Developers Hire VueJS Developers
Hire VueJS Developers Hire Full Stack Developers
Hire Full Stack Developers Hire Back End Developers
Hire Back End Developers Hire Front End Developers
Hire Front End Developers AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting
AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting Healthcare App Development
Healthcare App Development EHR Software Development
EHR Software Development Healthcare AI Chatbot Development
Healthcare AI Chatbot Development Telemedicine App Development Company
Telemedicine App Development Company Medical Billing Software Development
Medical Billing Software Development Fitness App Development
Fitness App Development RPM Software Development
RPM Software Development Medicine Delivery App Development
Medicine Delivery App Development Medical Device Software Development
Medical Device Software Development Patient Engagement Software Solutions
Patient Engagement Software Solutions Mental Health App Development
Mental Health App Development Healthcare IT Consulting
Healthcare IT Consulting Healthcare CRM Software Development
Healthcare CRM Software Development Healthcare IT Managed Services
Healthcare IT Managed Services Healthcare Software Testing services
Healthcare Software Testing services Medical Practice Management Software
Medical Practice Management Software Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services
Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services IoT Solutions for Healthcare
IoT Solutions for Healthcare Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services
Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services Lending Software Development Services
Lending Software Development Services Payment Gateway Software Development
Payment Gateway Software Development Accounting Software Development
Accounting Software Development AI-Driven Banking App Development
AI-Driven Banking App Development Insurance Software Development
Insurance Software Development Finance Software Development
Finance Software Development Loan Management Software Development
Loan Management Software Development Decentralized Finance Development Services
Decentralized Finance Development Services eWallet App Development
eWallet App Development Payment App Development
Payment App Development Money Transfer App Development
Money Transfer App Development Mortgage Software Development
Mortgage Software Development Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development
Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development Wealth Management Software Development
Wealth Management Software Development Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development
Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development Neobank App Development
Neobank App Development Stock Trading App Development
Stock Trading App Development AML software Development
AML software Development Web3 Wallet Development
Web3 Wallet Development Robo-Advisor App Development
Robo-Advisor App Development Supply Chain Management Software Development
Supply Chain Management Software Development Fleet Management Software Development
Fleet Management Software Development Warehouse Management Software Development
Warehouse Management Software Development LMS Development
LMS Development Education App Development
Education App Development Inventory Management Software Development
Inventory Management Software Development Property Management Software Development
Property Management Software Development Real Estate CRM Software Development
Real Estate CRM Software Development Real Estate Document Management Software
Real Estate Document Management Software Construction App Development
Construction App Development Construction ERP Software Development
Construction ERP Software Development





