Wearable Medical Devices in 2025: Statistics, Trends, and Future Impact on Healthcare
- August 21, 2025
-
1826 Views
- by Ishan Vyas
Wearable medical devices in 2025 have evolved from being just fitness trackers to bona fide healthcare tools, powered by AI sensors to track vitals, sleep, and glucose, supporting patient self-care and seamless data integration.
With the total market valued over $40 billion, wearable medical devices enhance patient engagement, while medical device software ensures secure data transfer, lowering costs and enabling preventive, technology-driven healthcare worldwide.
Wearable Medical Device Market Statistics
Global Market Size
The worldwide market for wearable medical devices has been estimated to be worth $42.68 billion in 2024, and it is expected to increase to $53.73 billion in 2025. According to the predictions of the industry experts, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR )of approximately 25.90% is expected from 2025 to 2034, which will place the segment among the leaders in the fastest-growing market of healthcare technology.
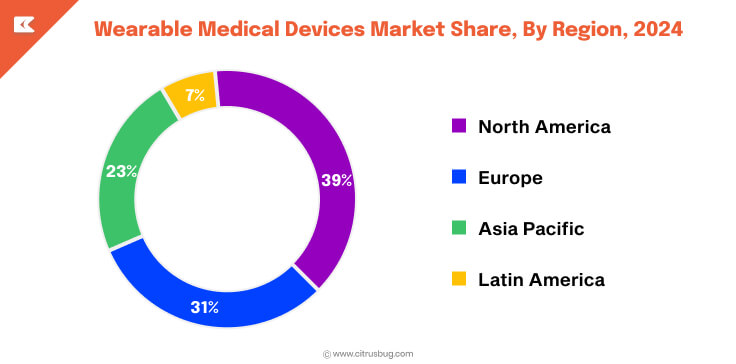
Regional Market Distribution
- North America leads the global wearable medical devices market with a 39% share, due to the increasing prevalence of diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and cancer within this region.
- Europe captures 31% of the global market, backed by well-established healthcare systems and increasing government initiatives toward digital health.
- Asia-Pacific holds the 23% market position, but it is considered the fastest-growing market at a CAGR of 28.4%, driven by various internal factors such as healthcare awareness, population growth, and increasing use of smart devices.
- Latin America holds the 7% market segment, but it is showing significant growth in the market due to improvements in its healthcare system, coupled with increasing incidences of chronic diseases leading to greater need for continuous monitoring options.
Types of Wearable Medical Devices in 2025
Smartwatches: The segment of wearable medical devices is led by smartwatches, which are valued at $33.58 billion in 2024, with a forecast to grow to $105.20 billion by 2032.
In addition to their multifunctionality, such as measuring the pulse, electrocardiogram (ECG), oxygen level, and stress, they are the most widely used medical devices that can be worn anywhere on the globe.
Fitness Trackers: The global fitness tracker market is valued at $60.9 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach $162.8 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 18.0% from 2025-2030.
The Fitness Trackers consist of smart bands that provide association for the physical activities, sleep, heart rate, and several other fitness data. These devices are connected to either a smartphone or the Internet to share data with other fitness lovers.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device market size was valued at $5.36 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach nearly $10.65 billion by 2034, with a growth rate of 7% from 2025 to 2034. Such devices allow on-the-spot glucose monitoring, thus minimizing the frequency of invasive finger-prick tests and facilitating better patient care.
Cardiac Monitoring Devices: Wearable heart monitoring devices market size was valued at $3.59 billion in 2024, and the industry experts’ analysis suggests that it will reach up to $9.02 billion by 2032, growing at the rate of 12.2% during the forecast period.
These devices allow continuous monitoring of heart rhythms, helping in the early detection of arrhythmias.
Smart Patches & Biosensors: Wearable biosensors are devices designed to be worn on the body to monitor various physiological parameters, activities, and environmental factors in real-time. The size of the wearable biosensors market was worth $30.50 billion in 2024, and the global revenue for wearable biosensors is projected to increase at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% between 2025 and 2032, amounting to almost $56.88 billion.
While hardware categories define the scope of wearable medical devices, it is the software layer that transforms raw data into actionable healthcare insights.
Role of Medical Device Software in Data Integration
Medical device software acts as the critical bridge between wearable hardware and healthcare systems, translating raw sensor data into actionable clinical insight. This sophisticated software ecosystem has been reengineering the flow of patient data through the healthcare continuum, making it synonymous with seamless integration between patients, devices, and care providers.
Software Architecture and Data Processing
The backbone of wearable medical devices lies in their software architecture, which specifies the way data is recorded, processed, and transmitted. Modern medical device software utilizes cloud infrastructure and edge computing, ensure fast, accurate, and reliable handling of health data.
Efficient data processing algorithms convert the raw signals into meaningful clinical metrics. By using machine learning and advanced AI algorithms, these systems enable healthcare providers to detect abnormal conditions at an early stage and provide a treatment plan that helps in the patient’s well-being.
Interoperability and Standards Compliance
Interoperability is a key element to making wearable medical devices interoperable with various healthcare systems. There are protocols, like HL7 and FHIR, that help establish data exchange encountered regularly, reducing fragmentation and enabling collaboration between users (health care providers and patients) with various platforms and devices.
Meeting global standards for health and safety goes a long way in building trust for the use of wearables globally. The absence of data interoperability leads to data being locked up in silos, thus limiting its value for clinical use. Compliance with strong frameworks contributes to the making of healthcare insights that can be relied upon, verified, and even used as a guide in decision-making across the entire healthcare ecosystem.
Real-Time Analytics and Clinical Decision Support
Medical device software converts continuous data streams into real-time analytics that show results for healthcare professionals to take action. Wearable devices collect vitals & alert clinical staff in real-time when abnormal conditions arise, allowing for a timely response for lower risk of complications.
Beyond alerts, advanced clinical decision support systems (CDSS) are integrated into all wearable devices and use AI algorithms to recommend treatment changes. This integration allows physicians to personalize therapies, modify drug doses, prevent emergencies, and turn wearable data into the cornerstone of evidence-based, precision healthcare.
Data Security and Privacy Protection
Because of the sensitivity of healthcare data, the security must be very strong in the software of medical devices. Part of the security is encrypted communication, secure APIs, and multi-layer authentication, which protects patient information from breaches and at the same time assures compliance with various regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
Privacy protection, in general, is also extended to data ownership and consent management. The patients are the owners of their health data and are allowed to decide who will have access and how. Such approaches not only build trust but also encourage the use of wearable medical technologies.
Integration with Healthcare Workflows
Wearable devices have to be integrated in a way that they are a part of the current healthcare workflows if they want to be of any use. The software in medical devices that helps hospitals communicate with EHRs, hospital dashboards, telemedicine platforms, etc., keeps the clinicians informed with real-time data without the need to change their daily routines.
Such an efficient integration minimizes the disruption of the workflow, reduces the administrative burden, and gives the care teams the possibility to use the data obtained from the wearables without complicating the process further. By incorporating into the established processes, wearable technologies not only become a source of the patient-centered care, but also become an instrument to accelerate the digital transformation in healthcare.
Latest Trends in Wearable Medical Devices
Smart Rings
One of the hottest wearable trends is smart rings. The U.S. will probably generate $190 million by 2025, while the total world shipments will likely increase at a 17% CAGR until 2028. IDC forecasts that the volume of smart rings to be shipped internationally will be 3.1 million units by 2028. It is a device that can make more of a fashion statement but still have the health tracking functions.
Smart Glasses
Smart medical glasses are becoming popular for telemedicine, diagnostics, and remote surgeries. The global market for smart glasses is expected to reach $16.74 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 10.51%. The smart glasses market is worth $ 6.16 billion in 2024. The demand for smart glass is growing because of the various features such as hands-free operation, increased efficiency, use in surgery, and more.
VR Headsets
VR technologies in healthcare are mostly used in medical training, patient treatment, and surgical planning. The global virtual reality (VR) in healthcare market size was valued $3.12 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow up to $46.37 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 35.1% during the forecast period.
North America have the major share of the market of 37.5%. Additionally, the U.S. virtual reality in healthcare market is predicted to grow significantly, reaching an estimated value of USD 8,956.0 million by 2032.
Challenges and Limitations of Wearable Medical Devices
Accuracy and Reliability Issues
- Wearable medical equipment is usually equipped with sensors; however, these sensors may deliver different values due to changes in skin tone, movement, or placement errors.
- The occurrence of false alarms or the provision of inaccurate data may cause patients as well as healthcare workers to be misled, and as a consequence, there will be a problem in trusting the devices.
Data Overload and Interpretation Challenges
- Continuous surveillance generates a huge amount of patient data, which can overload the healthcare system if it is not properly filtered and contextualized.
- Doctors and physicians might struggle to distinguish between clinically significant alerts and non-critical fluctuations.
Integration Barriers with Healthcare Systems
- Some wearable devices are not even partially compatible with existing electronic health records (EHRs) or hospital IT infrastructures.
- The absence of uniform interoperability protocols not only hinders the smooth integration of devices but also lowers the productivity of the healthcare system.
Privacy and Security Concerns
- The gadgets are targeted by hackers who want to illegitimately access the private health information that the devices collect.
- The need for developers and healthcare IT consultants to meet the requirements of HIPAA, GDPR, and other data protection regulations.
High Costs and Affordability Gap
- Medical-grade, advanced wearable medical devices are usually expensive, which its not easily accessible for people with low income.
- Constant hardware and software update leads to higher costs in the long run, as patients may have to change or upgrade their devices more frequently than they initially thought.
Battery Life and Usability Limitations
- Continuous tracking of data, especially for advanced features like ECG or glucose monitoring, drains battery at a faster rate, and as a result, users have to recharge their devices more frequently.
- Insufficient battery management can partially or entirely interrupt the follow-up of the patient’s health history.
Limited Clinical Validation
- A lot of wearable devices undergo a very rapid development process, and only a small portion of them are subjected to large-scale clinical testing, resulting in an uncertain medical accuracy of these devices.
- Without strong proof provided, physicians might not rely completely on information generated by these devices while making crucial decisions.
Benefits of Wearable Medical Devices
- Real-time continuous vital signs monitoring.
- Alerting the presence of diseases and health risks at an early stage.
- Provision of health and lifestyle suggestions that are customized by the patient.
- Increased patient engagement in self-care.
- Remote monitoring is used by healthcare professionals.
- Treatment of chronic diseases via health conditions continues effectively.
- Overall, healthcare costs are reduced.
- Provision of support for physical activities, sleep patterns, and stress level monitoring.
- Clinical decision-making that relies on data collected is accurate.
- Easily and smoothly complementary with Health Information Systems as well as Telemedicine.
Conclusion
Wearable medical devices revolutionize the healthcare system, combining data collection in real-time and AI-powered insight.
Their ability to monitor vitals throughout the time and being able to work with medical device software permits simple data transfers, prevention of treatment, and greater satisfaction of patients, which is the basis for the unparalleled connection between people and healthcare professionals.
The fast-growing market is bringing about advancements like biosensors, smartwatches, and VR applications, which are the primary driving force behind a new age in connected healthcare.
These devices not only improve the treatment and diagnosis process but also cut costs and allow healthcare to a wider range of patients.
Therefore, the future of medicine is in the use of these wearable medical devices, which make personalized treatment plans and make your healing journey proactive.




 SaaS Development
SaaS Development Web Application Development
Web Application Development Mobile Application Development
Mobile Application Development Custom Software Development
Custom Software Development Cloud Development
Cloud Development DevOps Development
DevOps Development MVP Development
MVP Development Digital Product Development
Digital Product Development Hire Chatbot Developers
Hire Chatbot Developers Hire Python Developers
Hire Python Developers Hire Django Developers
Hire Django Developers Hire ReactJS Developers
Hire ReactJS Developers Hire AngularJS Developers
Hire AngularJS Developers Hire VueJS Developers
Hire VueJS Developers Hire Full Stack Developers
Hire Full Stack Developers Hire Back End Developers
Hire Back End Developers Hire Front End Developers
Hire Front End Developers AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting
AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting Healthcare App Development
Healthcare App Development EHR Software Development
EHR Software Development Healthcare AI Chatbot Development
Healthcare AI Chatbot Development Telemedicine App Development Company
Telemedicine App Development Company Medical Billing Software Development
Medical Billing Software Development Fitness App Development
Fitness App Development RPM Software Development
RPM Software Development Medicine Delivery App Development
Medicine Delivery App Development Medical Device Software Development
Medical Device Software Development Patient Engagement Software Solutions
Patient Engagement Software Solutions Mental Health App Development
Mental Health App Development Healthcare IT Consulting
Healthcare IT Consulting Healthcare CRM Software Development
Healthcare CRM Software Development Healthcare IT Managed Services
Healthcare IT Managed Services Healthcare Software Testing services
Healthcare Software Testing services Medical Practice Management Software
Medical Practice Management Software Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services
Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services IoT Solutions for Healthcare
IoT Solutions for Healthcare Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services
Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services Lending Software Development Services
Lending Software Development Services Payment Gateway Software Development
Payment Gateway Software Development Accounting Software Development
Accounting Software Development AI-Driven Banking App Development
AI-Driven Banking App Development Insurance Software Development
Insurance Software Development Finance Software Development
Finance Software Development Loan Management Software Development
Loan Management Software Development Decentralized Finance Development Services
Decentralized Finance Development Services eWallet App Development
eWallet App Development Payment App Development
Payment App Development Money Transfer App Development
Money Transfer App Development Mortgage Software Development
Mortgage Software Development Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development
Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development Wealth Management Software Development
Wealth Management Software Development Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development
Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development Neobank App Development
Neobank App Development Stock Trading App Development
Stock Trading App Development AML software Development
AML software Development Web3 Wallet Development
Web3 Wallet Development Robo-Advisor App Development
Robo-Advisor App Development Supply Chain Management Software Development
Supply Chain Management Software Development Fleet Management Software Development
Fleet Management Software Development Warehouse Management Software Development
Warehouse Management Software Development LMS Development
LMS Development Education App Development
Education App Development Inventory Management Software Development
Inventory Management Software Development Property Management Software Development
Property Management Software Development Real Estate CRM Software Development
Real Estate CRM Software Development Real Estate Document Management Software
Real Estate Document Management Software Construction App Development
Construction App Development Construction ERP Software Development
Construction ERP Software Development