How AI Is Transforming Mental Health Diagnosis: Key Benefits and Applications
- September 29, 2025
-
751 Views
- by Ishan Vyas
Table of Contents
- Why Mental Health Diagnosis Need AI
- Key Pain Points in Mental Health Diagnosis
- Can AI Diagnose Mental Health?
- How AI Is Used in Mental Health Diagnosis and Therapy
- Benefits of AI in Mental Health Diagnosis
- Addressing Concerns: Ethics, Privacy, and Trust
- Future of AI in Mental Health Diagnosis and Treatment
- How Custom AI Software Development Can Help
- Conclusion
- FAQs on AI in Mental Health Diagnosis

Mental health disorders are among the leading causes of disability worldwide, still diagnosis is often slow, inconsistent, and limited by a shortage of professionals. People wait weeks to be assessed and in most cases, the disease is undetected until it’s too late. AI in mental health diagnosis is a bridge to these gaps by making the process faster, more consistent and more accessible.
AI systems are helping clinicians in identifying patterns through speech analysis, behavior, medical records, and even wearable data. They do not substitute physicians or therapists but provide them with a strong means to enhance their accuracy, minimize delays, and increase access to care.
Why Mental Health Diagnosis Need AI
There is a rising number of mental illnesses in the world, but diagnosis is often in demand. The traditional evaluation methods rely primarily on self-reporting and doctor observation, which are subjective and unreliable, particularly when it comes to patients. In the U.S., nearly 1 in every 5 adults becomes mentally ill each year and the majority of them are not diagnosed early or do not receive treatment.
Hospitals and clinics receive significant amounts of data, including from wearable devices and electronic health records, but they lack effective tools to evaluate such information. Mental health diagnosis with AI assists in interpreting this information. It recognizes the minor patterns, raises red flags, and assists clinicians in making quicker and more effective decisions.
There are a large number of areas that lack access to trained mental health facilities. The AI-generated technologies, which include chatbots and predictive analytics, can serve more underserved regions and decrease clinician workloads. This is the way AI is turning into a vital part of contemporary mental health care due to speed, consistency, and scalability.
Key Pain Points in Mental Health Diagnosis
The diagnosis of mental health faces numerous critical issues that impact the quality of its results, speed, and patients. Being conscious of these pain points can offer a chance to make AI a worthy solution.
Delayed or Missed Diagnoses
The majority of mental disorders go unnoticed for months. There are subtle symptoms that are hard to notice and lengthy queues of assessments worsen the situation. That delay complicates early intervention and may result in more severe issues over time. It also increases the emotional and financial burden of patients and families.
Subjective Clinical Evaluations
Diagnosis relies heavily on clinician judgment and patient self-reporting. Differences in training, perspective, or personal bias can lead to inconsistent evaluations and treatment decisions across providers. Subjective assessments also make it challenging to track progress objectively over time.
Shortage of Mental Health Professionals
The number of trained psychiatrists and psychologists is not enough to meet growing demand. It affects rural and underserved areas the most, which subjects patients to the risk of inaccessible quality and timely care. This shortage normally causes the overworking of the clinician and, later on, the waiting time, which influences the overall quality of care in a negative manner.
Data Overload and Underuse
Clinics receive large volumes of data on EHRs, questionnaires, and wearable devices. However, when these data points are not properly analyzed with effective tools, critical patterns that would help in the diagnosis are frequently overlooked. There are numerous hidden insights that exclude individual care and early detection of developing issues.
High Costs and Limited Access
The conventional diagnostic tests and treatment sessions are costly and need repetition. A lot of patients are not able to afford care, and remote or low-resource regions have a limited access to services. High costs also discourage preventive care, increasing the likelihood of chronic or severe mental health issues.
Can AI Diagnose Mental Health?
AI helps clinicians detect early signs of mental health problems, give decision support, and increase diagnostic accuracy. Through the analysis of the speech, facial expressions, patient records, and sensor data, AI can draw attention to minor signs that could otherwise remain unnoticed. It serves as an enabling tool that can assist in prioritizing the attention of patients who require urgent care without neglecting the role of human judgment in care.
1. Early Detection: AI identifies subtle changes in behavior, speech, and activity, helping clinicians spot conditions sooner.
2. Decision Support: AI interprets patient data and can give actionable data to make more comprehensive judgments.
3. Continuous Monitoring: AI tracks the progress based on digital health data and mobile applications to make timely changes to treatment regimens. It also enhances patient engagement characteristics as it keeps individuals actively engaged in their care.
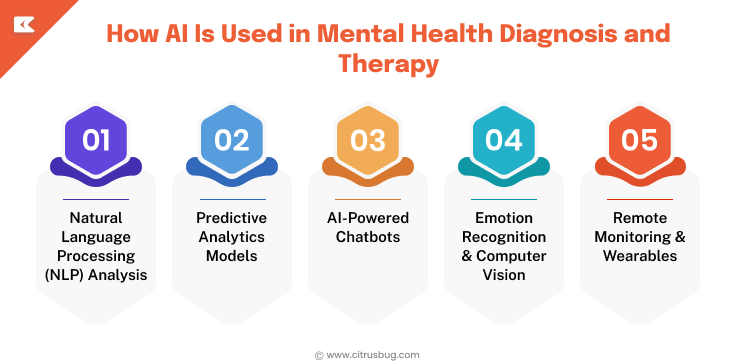
How AI Is Used in Mental Health Diagnosis and Therapy
Here are concrete applications where AI in mental health diagnosis shines:
Natural Language Processing (NLP) Analysis
This is a type of AI that analyzes speech and text to identify subtle indicators of depression, stress, or risk of self-harm to assist clinicians in recognizing the mental conditions of patients better.
Predictive Analytics Models
AI model analyzes historic patient records, including medical history, lifestyle behavior, and demographic data, in order to determine those at risk before the symptoms worsen and take actions to intervene in time.
AI-Powered Chatbots
Smart chatbots can offer patients long-term screenings, regular check-ups and directed therapy activities that keep them adherent to the treatment plans in between therapy sessions.
Emotion Recognition & Computer Vision
The AI can recognize facial expressions, voice tone, or gestures that can be associated with mood changes, which can help a clinician track an emotional status throughout the course of treatment and modify the therapy accordingly.
Remote Monitoring & Wearables
AI monitors sleep behaviors, physical exercise and physiological data to determine the level of mental health in real time beyond the clinic, and provides clinicians with useful data in real time.
The following applications demonstrate the intersection of AI in mental health diagnosis and treatment: helping to make appropriate diagnosis, improving therapy sessions, and providing an opportunity to monitor patients. Each solution can be customized in healthcare apps to improve outcomes, efficiency, and overall patient engagement.
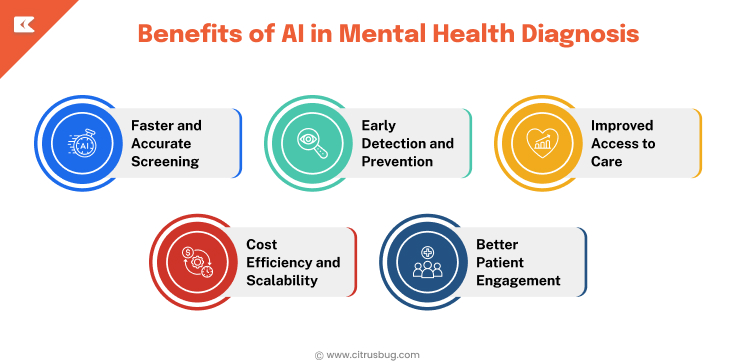
Benefits of AI in Mental Health Diagnosis
Faster and Accurate Screening
AI tools demonstrate high accuracy in studies. For example, multimodal models analyzing EEG and speech data can diagnose depression with around 97.5% accuracy.
Early Detection and Prevention
AI is capable of monitoring any inconspicuous behavioral or physiological changes before the manifestation of the full symptoms. Timely intervention can result in improved patient outcomes.
Improved Access to Care
Patients can be assisted with screening and help without necessarily consulting a specialist through healthcare chatbots, mobile applications, and remote monitoring, which can enhance their accessibility in rural and underserved regions.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
Custom AI solutions minimize the time required to conduct repetitive manual evaluations, run 24/7, and process high patient volumes without affecting costs in a linear manner.
Better Patient Engagement
AI tools that monitor progress, provide timely check-ins, and personalize communication help patients stay involved. Modern generative AI solutions for healthcare enhance therapy and engagement through interactive support.
Addressing Concerns: Ethics, Privacy, and Trust
Data Privacy & Compliance
Any AI application should be in accordance with HIPAA, GDPR, or other local laws. The information about mental health is very sensitive. It therefore needs to be stored securely, access needs to be controlled and auditing needs to be done appropriately to maintain patient confidentiality.
Reducing Bias in AI
The training data of AI must be varied, representative and inclusive of every population. Otherwise, patients who belong to underrepresented groups can be misdiagnosed by other models, which results in the unequal provision of care and raises serious ethical issues.
Explainability & Transparency
Clinicians and patients should know the way AI arrives at its decisions. Black-box models may decrease trust; hence, it is important to have clear explanations, visualizations, or reasoning to enable mass adoption and trust.
Human Oversight
AI must serve clinicians, not to substitute them. Diagnosis requires empathy, understanding of context, and human judgment, which AI alone cannot fully replicate or replace in mental health care.
Expert Guidance
Collaboration with healthcare AI consulting professionals can ensure the application of ethics, right compliance, continuous monitoring, and risk-free introduction of AI in the mental health procedures.
Future of AI in Mental Health Diagnosis and Treatment
Advancements in AI are improving diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment, and expanding access to mental health care.
- Research indicates that AI is accurate in identifying early signs of mental health conditions with up to 89 percent accuracy, and in some cases, AI will notify the human expert of the issue days before it. Depression and anxiety diagnosis tools have gone as far as 95 percent accuracy and have helped to make quicker and more informed clinical judgments.
- AI is capable of processing complex data, such as EEG, speech, and behavioral data, with high accuracy and can diagnose conditions, such as depression, and provide early intervention.
- AI-driven chatbots, mobile applications, and remote monitoring tools reach underserved or rural populations to provide them with mental health support and overcome the access barriers to mental health care and enhance AI in mental health applications.
- The telehealth systems have embedded AI to enable a clinician to conduct remote evaluation, administer virtual therapy, and track a patient effectively across geographic sites.
- Generative AI and large language models offer interactive therapy, customized instructions, and conversation activities to make the process more engaging for the patient.
- Advanced wearables and sensors track sleep, activity, and physiological signals in real-time, giving clinicians actionable insights for continuous, proactive mental health management.
How Custom AI Software Development Can Help
Custom AI development services are revolutionising mental health care by creating softwares that fits your business’ needs. Tailored software adapts to your workflow, patient data, and clinical goals, while improving diagnosis, monitoring, and therapy that off-the-shelf tools might not offer.
- AI models trained on your organization’s data improve prediction accuracy and highlight early warning signs in mental health care.
- Integration with EHRs, telehealth platforms, and mobile applications ensures smooth and seamless clinical workflows.
- Healthcare business intelligence software can be used with custom AI to interpret patient trends and monitor outcomes to optimize treatment plans in an efficient manner.
- Individual chatbots and interactive applications improve patient interaction and promote the use of treatment.
- Scalable solutions grow with your organization, handling increasing data volumes and evolving clinical requirements.
- In-built compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulations ensures sensitive patient data remains secure.
- The development of custom AI solutions can help healthcare providers become smarter, faster, and more personalized in their approach, which results in better patient outcomes and efficiency.
Conclusion
AI is redefining mental health diagnosis and treatment by providing faster detection, personalized interventions, and better access to care. These technologies are supporting clinicians while improving patient care with predictive analytics and NLP to generative AI and wearable devices.
At Citrusbug Technolabs, we specialize in customized AI mental health app development that creates intelligent applications for your organization’s needs. Healthcare providers can accelerate the adoption of AI technologies that increase clinicians’ diagnoses capabilities and workflows while providing smarter patient-centered care.
FAQs on AI in Mental Health Diagnosis
Can AI help detect mental health conditions in children and adolescents?
Yes, AI models can process behavioral patterns, data on speech and activities in young groups and detect early signs of conditions like ADHD, anxiety or depression. It has the potential to help clinicians intervene at an earlier stage.
How does AI differentiate between similar mental health disorders?
AI algorithms can process several data streams such as speech, facial expression, EHR records and wearable data to find minor variations between disorders that facilitate more precise diagnoses.
Can AI track the effectiveness of therapy over time?
Yes, AI-based systems can track patient reactions, contacts, and psychological indicators in real-time, which will allow determine the effectiveness of the treatment and allow clinicians to modify treatment schedules.
Can AI tools support remote mental health care effectively?
Yes, AI-based remote monitoring tools, chatbots, and apps allow patients to receive screenings, therapy exercises, and progress monitoring from anywhere, increasing access and continuity of care.




 SaaS Development
SaaS Development Web Application Development
Web Application Development Mobile Application Development
Mobile Application Development Custom Software Development
Custom Software Development Cloud Development
Cloud Development DevOps Development
DevOps Development MVP Development
MVP Development Digital Product Development
Digital Product Development Hire Chatbot Developers
Hire Chatbot Developers Hire Python Developers
Hire Python Developers Hire Django Developers
Hire Django Developers Hire ReactJS Developers
Hire ReactJS Developers Hire AngularJS Developers
Hire AngularJS Developers Hire VueJS Developers
Hire VueJS Developers Hire Full Stack Developers
Hire Full Stack Developers Hire Back End Developers
Hire Back End Developers Hire Front End Developers
Hire Front End Developers AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting
AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting Healthcare App Development
Healthcare App Development EHR Software Development
EHR Software Development Healthcare AI Chatbot Development
Healthcare AI Chatbot Development Telemedicine App Development Company
Telemedicine App Development Company Medical Billing Software Development
Medical Billing Software Development Fitness App Development
Fitness App Development RPM Software Development
RPM Software Development Medicine Delivery App Development
Medicine Delivery App Development Medical Device Software Development
Medical Device Software Development Patient Engagement Software Solutions
Patient Engagement Software Solutions Mental Health App Development
Mental Health App Development Healthcare IT Consulting
Healthcare IT Consulting Healthcare CRM Software Development
Healthcare CRM Software Development Healthcare IT Managed Services
Healthcare IT Managed Services Healthcare Software Testing services
Healthcare Software Testing services Medical Practice Management Software
Medical Practice Management Software Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services
Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services IoT Solutions for Healthcare
IoT Solutions for Healthcare Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services
Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services Lending Software Development Services
Lending Software Development Services Payment Gateway Software Development
Payment Gateway Software Development Accounting Software Development
Accounting Software Development AI-Driven Banking App Development
AI-Driven Banking App Development Insurance Software Development
Insurance Software Development Finance Software Development
Finance Software Development Loan Management Software Development
Loan Management Software Development Decentralized Finance Development Services
Decentralized Finance Development Services eWallet App Development
eWallet App Development Payment App Development
Payment App Development Money Transfer App Development
Money Transfer App Development Mortgage Software Development
Mortgage Software Development Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development
Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development Wealth Management Software Development
Wealth Management Software Development Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development
Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development Neobank App Development
Neobank App Development Stock Trading App Development
Stock Trading App Development AML software Development
AML software Development Web3 Wallet Development
Web3 Wallet Development Robo-Advisor App Development
Robo-Advisor App Development Supply Chain Management Software Development
Supply Chain Management Software Development Fleet Management Software Development
Fleet Management Software Development Warehouse Management Software Development
Warehouse Management Software Development LMS Development
LMS Development Education App Development
Education App Development Inventory Management Software Development
Inventory Management Software Development Property Management Software Development
Property Management Software Development Real Estate CRM Software Development
Real Estate CRM Software Development Real Estate Document Management Software
Real Estate Document Management Software Construction App Development
Construction App Development Construction ERP Software Development
Construction ERP Software Development