Digital Payment Statistics: Global Trends, Growth Rate, and Future Outlook
- January 23, 2026
-
425 Views
- by Ishan Vyas
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Global Digital Payments: Market Size and Forecasts
- Digital Payment Adoption: Global Usage and Penetration Trends
- Digital Payment Adoption Statistics in Different Industries
- Digital Payment Methods: What People Use the Most?
- Key Drivers Behind Digital Payment Growth
- Challenges and Security Issues in Digital Payments
- Traditional payments vs. digital payments: 5 key differences
- Future Outlook: Digital Payments Beyond 2026
- Conclusion

Introduction
Digital payments have disrupted the financial landscape across the world over the last 10 years. What started as a convenient alternative for cash and cards has now become indispensable to global commerce, financial inclusion and overall economic development.
When mobile wallets, contactless payments, real-time bank transfers and integrated payment experiences are responsible for facilitating trillions of dollars in transactions each year among consumers, businesses and governments.
In this post, we will discuss the most important digital payment statistics, worldwide trends, and future progression of this ever-growing field.
Global Digital Payments: Market Size and Forecasts
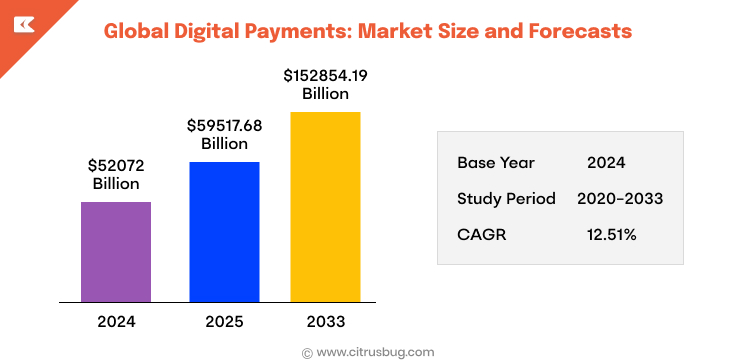
- The global digital payments market reached USD 52,072 billion in 2024, indicating the huge popularity of cashless payments worldwide. Rising adoption is being fueled by greater smartphone use and e-commerce.
- The market is expected to expand in 2025, increasing to USD 59,517.68 billion on the back of increasing consumer reliance on digital payment systems. Businesses are starting to use digital payment methods for quicker payments.
- The global digital payment market is estimated to reach USD 152,854.19 billion by the end of 2033, indicating massive long-term expansion. This is all greatly fueled by rapid fintech innovation, and global digitization.
- The market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 12.51% through 2025-2033, with steady and good growth. Government programs and advancements in payment infrastructure also contribute to this development, according to long-term digital payment statistics.
Digital Payment Adoption: Global Usage and Penetration Trends
Understanding how users across the world adopt digital payments is essential for readers who want to see who’s using what and where digital payment adoption is accelerating fastest. These digital payment statistics highlight both overall usage levels and regional behavior patterns across consumers and markets.
Digital Payments Powering Global Growth
Digital payments such as mobile wallets, card-based payments and settlements, online bank transfers and real-time digital payment systems are the preferred mode of everyday transactions at all levels. Convenience, speed, security and easy integration with e-commerce and mobile channels have made customers of every age group, income level and geography.
Key Adoption Highlights
Global User Growth
- In 2024, around 4.3 billion people worldwide used some form of digital payment. This means that more than half the population of the world has made cashless payments for at least the majority of their daily transactions, as highlighted by recent digital payment statistics.
- The momentum continued to grow into 2025. According to market research, more than 5.6 billion people were using digital payment services in the year, highlighting how they are in our daily lives.
- Looking ahead, projections indicate that the number of digital payment users could rise to about 6.2 billion in 2026. The majority of the growth in this area is predicted to come from Asia, Africa, and Latin America, where digital payments are increasing the availability of financial services and helping to increase financial access.
Consumer Behavior Trends
- In 2023, more than 73% of the adult population relied on at least one method of digital payment. This reflects the widespread acceptance worldwide of electronic transactions and cashless methods.
- Many of the global population have made use of mobile payment at least once, or even regularly, highlighting a shift in payment behavior away from cash and cards.
Regional Penetration Statistics
China
- China has around 1,022 million people using mobile payments. It’s one of the largest digital payment markets around the globe.
- The use of mobile payments in China is very large and is estimated to be around 90% of people, thanks to platforms such as Alipay and WeChat Pay.
India
- India is experiencing an explosion in the growth of digital and payment systems, which have processed billions of transactions every year through digital channels like UPI. According to data published by NPCI, there were over 172 billion UPI transactions in 2024. This accounts for an increase of 46% on a YoY basis, and a significant usage of mobile phones.
- In the first half of 2025, digital payments represented almost 99.8% of the total transactions in India, which demonstrates how rapidly cashless payment methods have surpassed traditional methods of payment.
United States
- Around 70% of U.S. adults use some type of digital payment that includes credit/debit cards, online banking transactions, digital wallets and contactless payment methods.
- Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) use is the highest among people between the ages of 25 and 44. BNPL remains a small portion of 5-6% of all U.S. online shopping; that is a sign of a niche but growing acceptance.
Other Regions
- Southeast Asia is one of the most rapidly growing digital payment regions, and adoption is expected to increase quickly until 2025.
- More than 40% of the population in Sub-Saharan Africa uses digital financial services, mostly mobile-based payment systems.
- More than 60% of European customers use digital payment methods to pay for online purchases.
Digital Payment Adoption Statistics in Different Industries
The graph shows that digital transfer services lead the adoption of digital payments at 75%, which highlights their significant role in online and cross-border money transfers. It is followed closely by peer-to -peer transfers, which are 71%, and subscription service payments with 70% that show the wide usage for both recurring and everyday transactions.
In-app purchases and e-commerce transactions follow, with 60%, highlighting their vital role in providing online shopping and mobile services. These sectors are major drivers for the development of a digital economy, thanks to the speed and ease with which financial transactions can be completed.
Utility bill payments account for 50% adoption, indicating a balanced mix of traditional and digital payment usage. Similarly, B2B payments at 49% show that nearly half of business transactions are now conducted digitally.
In-store payments come in at 45% acceptance, followed by travel and hospitality at 40%, indicating reasonably high levels of digital payment adoption for physical goods and services. These industries are slowly turning digital instead of only cash or cards.
Healthcare services have a slower rate of adoption at 30% because of operational and regulatory difficulties. Point-of-sale (POS) transactions remain the least popular at 28%, suggesting significant potential for future growth in digital payment adoption at checkouts in retail stores.
Digital Payment Methods: What People Use the Most?
The growing popularity of digital forms for payment has developed as people put more value on speed, convenience, and security. As per digital payment statistics, credit/debit card payments and e-wallets are the major players in online transactions, and people are gradually adopting newer methods at an exponential rate.
1) Digital Wallets
Digital wallets are the leading e-commerce tools worldwide, accounting for 50% of total transaction value in 2023. Some of the best-known are Google Pay, Apple Pay, PayPal and Venmo. This propensity is also expected to rise, with 61% of digital wallets predicted by 2027.
2) Credit Cards
Credit cards are the world’s second most popular online payment method, capturing a 22% share of global e-commerce payments. Consumers are turning to credit cards more due to convenience, rewards and protections.
3) Debit Cards
Debit cards are in third place, with an estimated 12% of total e-commerce spend worldwide. Although they will remain widely accepted, their proportion is set to drop to around 8% by 2027 as other digital methods become increasingly popular.
4) Account-to-Account (A2A) Transfers
A2A payments, sending money directly from bank account to account (e.g., bank transfers/real-time payments), accounted for 7% of online payments in 2023. Their usage is forecasted to tick up slightly to 8% by 2027.
5) Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL)
BNPL services accounted for 5% of global e-commerce transactions in 2023, with shoppers able to split the payments into installments. According to digital payment statistics, this method is quickly becoming more popular, especially among younger consumers and for high-value purchases.
6) Cash on Delivery
Cash on delivery accounts for just 2% of global online payment volumes, which demonstrates the gradual decline of cash-based options. Its use is expected to decline further as access to digital payment improves.
7) Prepaid Cards
They accounted for only 1% of the value of online transactions worldwide in 2023 and their share is likely to stay low in the coming years.
Key Drivers Behind Digital Payment Growth
1) Smartphone and Internet Penetration
Adoption of smartphones has been a major enabler of growth in digital payment, offering use cases like mobile wallets and contactless payments, both for retail and online commerce. Increased deployment of 5G and mobile broadband makes transaction experiences faster and more secure.
2) COVID-19 & Shift to Contactless Payments
The pandemic accelerated the shift from cash to digital payments, particularly contactless cards and QR-based payments, which help reduce physical touchpoints at retail stores.
3) Fintech Innovation
Fintech apps (PayPal, Stripe, Square) and tech platforms (Apple Pay, Google Wallet) are pushing innovation with fintech app development, with features such as:
- Real-time transfers
- Biometric authentication
- AI-powered fraud prevention
These developments drive uptake by increasing ease of use, security and confidence.
4) Expansion of E-Commerce Platforms
The rise of e-commerce, which is expected to surpass $7.4 trillion in worldwide retail business by 2025, has driven digital payment adoption. Consumers prefer digital wallets and fast checkouts.
Challenges and Security Issues in Digital Payments
These challenges highlight that while digital payments offer convenience and speed, maintaining robust security measures and regulatory compliance is essential to protect users and sustain growth in the rapidly evolving digital payments ecosystem.
1) Rising Fraud and Cyber Threats
As more consumers use digital payment platforms, fraud attempts have increased. Common attacks include phishing, identity theft, and account takeovers.
For example, consumer fraud losses reached $12.5 billion in 2024, showing the financial impact of these risks highlighted by global digital payment statistics.
2) Need for Advanced Security Measures
To protect users, providers are adopting multi-factor authentication, AI-driven fraud detection, and biometric payment security.
These tools help detect suspicious activity in real time and reduce reliance on traditional passwords, balancing security with convenience.
3) Fragmented Regulatory Environments
Digital payments move across regions with different rules. The EU has strict data protection regulations (GDPR), whereas developing countries are still trying to develop such laws.
This regulatory fragmentation makes compliance complicated for globally operating firms.
4) Complexity of Cross-Border Payments
Differences in KYC/AML requirements, consumer protection laws, and data localization rules make international digital transactions difficult.
Harmonizing these regulations is challenging but essential for seamless global payment flows.
5) Continuous Need for Trust and Compliance
Security breaches or non-compliance can damage consumer trust and slow adoption.
Payment providers must invest in both technology and regulatory alignment to maintain confidence and ensure sustainable growth.
Traditional payments vs. digital payments: 5 key differences
Traditional payments and digital payments represent two different approaches to delivering financial services, each with distinct features, benefits, and limitations.
Here’s a quick overview of their key differences:
| Feature / Aspect | Traditional Payments | Digital Payments |
|---|---|---|
| Access and Availability | Services are offered via physical branches with limited working hours. In-person visits are usually required. |
Available 24/7 via mobile apps and websites. Over 70% of consumers in major markets regularly use digital and mobile payment channels. |
| Customer Interaction | Face-to-face interactions are preferred by older customers and small business owners for advice and complex transactions. |
Mostly automated using AI chatbots. Around 75% of banks are expected to integrate AI by 2025 for faster service. |
| Costs and Fees | Higher fees due to staff, branch maintenance, and out-of-network ATM charges. | Lower infrastructure costs enable minimal or no monthly fees and wider free ATM access. |
| Speed and Convenience | Cash and cheque transactions are slower and require physical visits. Cross-border payments take longer. |
Faster transactions; 70% of users find digital payments more convenient, reducing transaction time by up to 25 minutes. |
| Technology Use | Depends on legacy systems with physical security and compliance protocols. | Uses AI, biometrics, and fraud detection systems. Continuous monitoring enhances security but requires ongoing oversight. |
Future Outlook: Digital Payments Beyond 2026
1. Real-Time Payments Will Become the Global Default
Real-time payments are increasing in both developing and developed markets. The number of real-time transactions in payments is predicted to grow from 266.2 billion by 2023 to 575 billion by 2028. driven by systems such as UPI, Pix and Faster Payments.
This change indicates that instant, 24/7 cash transfers are increasingly replacing delayed settlement methods, such as traditional bank transfers.
2. Artificial Intelligence Will Power Smarter Payment Systems
AI will play an integral part in fraud detection, along with transaction routing and optimization of payments. According to forecasts from industry experts, AI-powered payment systems are predicted to affect the majority of the global transactions in e-commerce by the end of 2020, by utilizing automated decision-making.
Banks and payment providers are already integrating machine learning algorithms to decrease rates of false declines and increase approval rates.
3. Digital Wallets Will Become the Primary Payment Interface
Digital wallets will remain the most popular payment method for consumers across both stores and online platforms. In the middle-to-late 2020s, digital wallets are expected to be responsible for more than 60% of all global online transactions, a rise from around 50% in 2023.
Wallets are increasingly integrating identities, payments, loyalty, and financial services in one mobile-friendly interface.
4. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) Will Expand Gradually
According to the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) 2024 survey, 91% of central banks surveyed (out of 93) are exploring a central bank digital currency (retail, wholesale, or both). This includes research, planning, and early-stage development work, reflecting very broad global engagement in CBDC initiatives.
China’s cross-border CBDC platform (mBridge) has already processed over $55 billion in transactions, signaling growing real-world usage.
5. Cross-Border Digital Payments Will Become Faster and Cheaper
International payment systems are upgraded by collaboration among central bankers and fintech companies. New platforms are designed to cut the time to settle from days to minutes while decreasing the cost of processing and foreign exchange.
Global initiatives, led by BIS and its central bank partners, are exploring interoperable payment rails that can facilitate cross-border transfers.
6. Regulation and Infrastructure Will Continue to Evolve
Governments are rewriting payment laws to allow for new technology such as stablecoins and open banking as well as digital identity wallets. More clarity in the regulatory process will likely reduce the uncertainty in the marketplace and lead to greater innovation and improved consumer security.
The development of digital public infrastructure will continue to be a top priority for both developed and emerging economies.
Conclusion
Digital payments have become a key component in the world economy, fuelled by strong user acceptance as well as new technology and policy-based support. Digital payment statistics demonstrate rapid growth across different sectors, industries and payment methods such as wallets and instant payments, leading the way.
With the advancement of security, AI, and infrastructure improvement, payment app development is expected to play an important role in establishing more efficient, more secure, and accessible financial systems. The future of payment is clearly digital, connected, and user-centric.




 SaaS Development
SaaS Development Web Application Development
Web Application Development Mobile Application Development
Mobile Application Development Custom Software Development
Custom Software Development Cloud Development
Cloud Development DevOps Development
DevOps Development MVP Development
MVP Development Digital Product Development
Digital Product Development Hire Chatbot Developers
Hire Chatbot Developers Hire Python Developers
Hire Python Developers Hire Django Developers
Hire Django Developers Hire ReactJS Developers
Hire ReactJS Developers Hire AngularJS Developers
Hire AngularJS Developers Hire VueJS Developers
Hire VueJS Developers Hire Full Stack Developers
Hire Full Stack Developers Hire Back End Developers
Hire Back End Developers Hire Front End Developers
Hire Front End Developers AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting
AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting Healthcare App Development
Healthcare App Development EHR Software Development
EHR Software Development Healthcare AI Chatbot Development
Healthcare AI Chatbot Development Telemedicine App Development Company
Telemedicine App Development Company Medical Billing Software Development
Medical Billing Software Development Fitness App Development
Fitness App Development RPM Software Development
RPM Software Development Medicine Delivery App Development
Medicine Delivery App Development Medical Device Software Development
Medical Device Software Development Patient Engagement Software Solutions
Patient Engagement Software Solutions Mental Health App Development
Mental Health App Development Healthcare IT Consulting
Healthcare IT Consulting Healthcare CRM Software Development
Healthcare CRM Software Development Healthcare IT Managed Services
Healthcare IT Managed Services Healthcare Software Testing services
Healthcare Software Testing services Medical Practice Management Software
Medical Practice Management Software Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services
Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services IoT Solutions for Healthcare
IoT Solutions for Healthcare Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services
Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services Lending Software Development Services
Lending Software Development Services Payment Gateway Software Development
Payment Gateway Software Development Accounting Software Development
Accounting Software Development AI-Driven Banking App Development
AI-Driven Banking App Development Insurance Software Development
Insurance Software Development Finance Software Development
Finance Software Development Loan Management Software Development
Loan Management Software Development Decentralized Finance Development Services
Decentralized Finance Development Services eWallet App Development
eWallet App Development Payment App Development
Payment App Development Money Transfer App Development
Money Transfer App Development Mortgage Software Development
Mortgage Software Development Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development
Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development Wealth Management Software Development
Wealth Management Software Development Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development
Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development Neobank App Development
Neobank App Development Stock Trading App Development
Stock Trading App Development AML software Development
AML software Development Web3 Wallet Development
Web3 Wallet Development Robo-Advisor App Development
Robo-Advisor App Development Supply Chain Management Software Development
Supply Chain Management Software Development Fleet Management Software Development
Fleet Management Software Development Warehouse Management Software Development
Warehouse Management Software Development LMS Development
LMS Development Education App Development
Education App Development Inventory Management Software Development
Inventory Management Software Development Property Management Software Development
Property Management Software Development Real Estate CRM Software Development
Real Estate CRM Software Development Real Estate Document Management Software
Real Estate Document Management Software Construction App Development
Construction App Development Construction ERP Software Development
Construction ERP Software Development








