Top Innovations Shaping the Future of Mobile Applications and Development Practices
- December 19, 2024
-
4174 Views
- by Ishan Vyas
Table of Contents
Mobile devices such as smartphones have become an integral part of our lives. From paying bills and booking appointments to entertainment and shopping, an average person relies on their smartphone for a multitude of tasks. These capabilities wouldn’t be possible without the continuous evolution of mobile app development, which plays a crucial role in enhancing user experiences.
However, in the fast-paced tech world, innovation is constant. New advancements in mobile app development are not only transforming the way applications are built but also how they interact with devices. These innovations aim to improve functionality, increase efficiency, and offer users more personalized experiences.
In this article, we’ll explore some of the most exciting trends and technologies shaping the future of mobile applications and development practices.
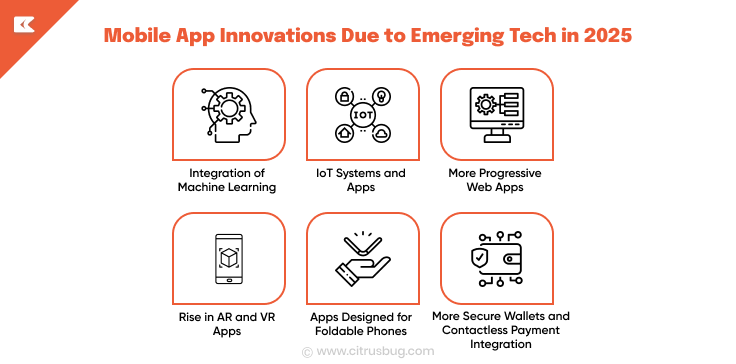
Mobile App Innovations Due to Emerging Tech in 2025
Integration of Machine Learning
Machine learning and artificial intelligence have taken the world by storm. Nowadays, you will find AI plastered on everything. It has literally become a marketing buzzword.
The interesting thing about AI is that it is still in its infancy. So, it is going to become better over time.
Current uses of AI and, by extension, machine learning include researching user data to find trends and patterns. This technology is also driving innovations in mobile app development through AI-driven features, such as targeted marketing and personalized recommendations.
The data collected about users is often related to geographical location, age, gender, and perceived wealth/spending capacity. Technologies like IP geolocation, information from sign-up/registration, and spending habits are used to train machine learning models.
We can expect future mobile apps to start learning about their users on their own and make autonomous decisions. These decisions can enhance the user experience.
The applications of machine learning are immense. However, what holds it back is the massive computing power required to implement it.
Presently, companies developing mobile applications use a different solution. They just program the app to collect and send data to a powerful server. The server trains the model using its massive computing power.
However, the drawback to this approach is that you cannot train models on individual people. You always need data from a large demographic to justify the computing costs. So, the models are always a bit general rather than specific.
Hopefully, in the near future, we won’t need such high computing power, which will enable even normal home devices, such as PCs and smartphones, to train personal machine-learning models with relative ease.
IoT Systems and Apps
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way devices interact with each other, creating an interconnected network that seamlessly shares data. What makes IoT unique is its reliance on smaller, less powerful devices designed to perform specific tasks efficiently, such as sending or receiving data and taking predefined actions.
Mobile applications are central to unlocking the full potential of IoT networks. These apps act as a bridge, connecting users to their smart devices and enabling advanced control and automation. For instance, mobile apps can harness smartphone sensors like gyroscopes, accelerometers, or NFC chips to interact with IoT ecosystems. Imagine your phone automatically notifying your car to start the engine and turn on the AC as you approach or controlling your smart home’s lighting and temperature from anywhere.
IoT-friendly apps go beyond basic connectivity. Developers are now focusing on creating centralized applications that allow users to manage multiple IoT devices through a single interface. These apps provide real-time data from all connected devices and enable users to customize settings or take manual actions.
For example, a mobile app for a smart home setup could let users monitor room temperatures, schedule appliances, or adjust lighting—all from their phones. As IoT technology continues to evolve, mobile app development is set to play an even bigger role in designing intuitive, user-friendly solutions that make managing IoT ecosystems effortless.
By integrating IoT capabilities into mobile app development, developers are not just building apps—they are creating the tools that will define how we interact with the digital world in the future.
More Progressive Web Apps
A progressive web app (PWA) is a special type of app that combines the best of native apps and websites. Websites have the advantage of being cross-platform. As long as the same browser is supported across all platforms, the website will run on it.
Apps, on the other hand, are better at using a device’s resources to do more complex tasks. However, they lack cross-platform compatibility and need to be developed separately for different systems.
A progressive web app combines the benefits of both approaches into one package. So, a PWA has enhanced access to a device’s resources like an app, but it is also cross-platform. This makes PWAs a popular choice for businesses looking to reach wider audiences without the need for separate native apps. Many developers now prefer PWAs for their efficiency and potential in cross-platform app development, ensuring a seamless user experience across devices and platforms.
More apps are now being made as PWAs, and this trend will continue in the future. One of the best examples of this is the use of the Flutter framework. With Flutter, devs can create apps for both iOS and Android using a single code base. React is another technology that is frequently used for PWA because it can be used to create both mobile application UI and web page UI. Many developers are now leveraging React Native for mobile app development to build efficient, cross-platform applications.
This kind of flexibility is great for the mobile device ecosystem as it means that more apps can be created for all operating systems.
Rise in AR and VR Apps
AR and VR technologies have become more common in recent years. Nowadays, you can use VR headsets with your smartphones to access VR content.
AR apps are much easier to use. They simply use smartphone cameras to project entities in the real world. These entities can be seen and interacted with through the smartphone screen.
Some companies, like Nintendo, have a neat AR feature where the AR data is stored on a QR code. An animated AR entity starts playing around on the screen when a device interacts with that code using a QR scanner.
AR apps are also used in engineering and assembly projects. Specific parts with QR codes on them are projected and shown in their correct location when scanned with smartphones.
In the future, you can expect more apps to be built for VR devices and more sophisticated AR apps.
Apps Designed for Foldable Phones
Foldable phones are a relatively new phenomenon. Introduced by Samsung to the world, flip phones are now more common and affordable. Recently, Huawei released a triple-fold phone, which can fold twice on itself and can be used in three different screen sizes.
Apps designed for such phones need to be responsive and change their UI according to the different screen sizes. The challenge here is adjusting to the square screen that forms when you only fold the phone once.
Most of our apps run on widescreen (16:9) or portrait mode (9:16). Foldable phones introduce a much older aspect ratio of 4:3. This ratio was present in old CRT televisions and monitors and has not been used regularly for over 15 years.
When you hire Mobile application developers, make sure they know how to improve the UI for this aspect ratio and ensure users have a good user experience.
More Secure Wallets and Contactless Payment Integration
Contactless payments are becoming more mainstream. There are several wallet apps available today in which you can store money digitally (through your bank) and pay online in supported stores. These wallets are also widely used with tools like online booking software, making payments faster and more convenient.
One of the features of wallet apps is the integration of QR codes and NFC (Near Field Communication) for contactless payments. Modern smartphones have NFC capability and are capable of using a QR scanner.
These two technologies allow wallet apps to transfer money to other wallets or banks after the necessary authorizations. Mobile application developers will need to include integrations and support in their apps for wallets.
The benefit of doing this is that the users will have a better experience, and they will be less likely to look for competitors.
One aspect of wallet apps is security. Mobile application devs will need to be careful that their integrations don’t bypass security measures. Most wallet apps like PayPal already have their own AI-based security systems, but developers should still be prudent in implementing their own.
Conclusion
The technology landscape is constantly changing, and mobile app development is no exception. With every passing year, advancements reshape the way applications are designed and built. To remain competitive, developers must keep pace with these changes, integrating new technologies and trends into their work.
Staying ahead requires a keen understanding of the latest developments and anticipating where the industry is headed. In this article, we explored key directions in mobile app development, including the growing influence of AI, the rise of IoT-integrated applications, the refinement of PWAs, and the increasing adoption of AR and VR technologies.
By incorporating these innovations into your applications, you can not only improve their functionality and user experience but also ensure they remain relevant and impactful in the years to come. Embracing these trends isn’t just about keeping up, it’s about leading the way in delivering cutting-edge mobile solutions.




 SaaS Development
SaaS Development Web Application Development
Web Application Development Mobile Application Development
Mobile Application Development Custom Software Development
Custom Software Development Cloud Development
Cloud Development DevOps Development
DevOps Development MVP Development
MVP Development Digital Product Development
Digital Product Development Hire Chatbot Developers
Hire Chatbot Developers Hire Python Developers
Hire Python Developers Hire Django Developers
Hire Django Developers Hire ReactJS Developers
Hire ReactJS Developers Hire AngularJS Developers
Hire AngularJS Developers Hire VueJS Developers
Hire VueJS Developers Hire Full Stack Developers
Hire Full Stack Developers Hire Back End Developers
Hire Back End Developers Hire Front End Developers
Hire Front End Developers AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting
AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting Healthcare App Development
Healthcare App Development EHR Software Development
EHR Software Development Healthcare AI Chatbot Development
Healthcare AI Chatbot Development Telemedicine App Development Company
Telemedicine App Development Company Medical Billing Software Development
Medical Billing Software Development Fitness App Development
Fitness App Development RPM Software Development
RPM Software Development Medicine Delivery App Development
Medicine Delivery App Development Medical Device Software Development
Medical Device Software Development Patient Engagement Software Solutions
Patient Engagement Software Solutions Mental Health App Development
Mental Health App Development Healthcare IT Consulting
Healthcare IT Consulting Healthcare CRM Software Development
Healthcare CRM Software Development Healthcare IT Managed Services
Healthcare IT Managed Services Healthcare Software Testing services
Healthcare Software Testing services Medical Practice Management Software
Medical Practice Management Software Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services
Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services IoT Solutions for Healthcare
IoT Solutions for Healthcare Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services
Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services Lending Software Development Services
Lending Software Development Services Payment Gateway Software Development
Payment Gateway Software Development Accounting Software Development
Accounting Software Development AI-Driven Banking App Development
AI-Driven Banking App Development Insurance Software Development
Insurance Software Development Finance Software Development
Finance Software Development Loan Management Software Development
Loan Management Software Development Decentralized Finance Development Services
Decentralized Finance Development Services eWallet App Development
eWallet App Development Payment App Development
Payment App Development Money Transfer App Development
Money Transfer App Development Mortgage Software Development
Mortgage Software Development Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development
Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development Wealth Management Software Development
Wealth Management Software Development Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development
Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development Neobank App Development
Neobank App Development Stock Trading App Development
Stock Trading App Development AML software Development
AML software Development Web3 Wallet Development
Web3 Wallet Development Robo-Advisor App Development
Robo-Advisor App Development Supply Chain Management Software Development
Supply Chain Management Software Development Fleet Management Software Development
Fleet Management Software Development Warehouse Management Software Development
Warehouse Management Software Development LMS Development
LMS Development Education App Development
Education App Development Inventory Management Software Development
Inventory Management Software Development Property Management Software Development
Property Management Software Development Real Estate CRM Software Development
Real Estate CRM Software Development Real Estate Document Management Software
Real Estate Document Management Software Construction App Development
Construction App Development Construction ERP Software Development
Construction ERP Software Development