AI Agents Statistics 2025: Adoption Rates, Market Insights, and Future Trends
- October 27, 2025
-
1768 Views
- by Ishan Vyas
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents are systems capable of performing tasks, making decisions, and engaging users independently, unlike traditional automation technologies that rely on human input for analysis or taking actions. From personal assistants to enterprise solutions, these AI solutions have increasingly become key parts of everyday operations for people and companies alike.
They play an ever-increasing role across industries, improving customer service, streamlining workflows and driving data-driven decision making. From AI agents in business operations to new innovations like creating AI chatbots, these technologies are revolutionizing how work gets done and value is created. In this article we’ll look into AI Agents statistics: their adoption rates, market insights and key trends shaping their evolution until 2025 and beyond.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are intelligent software systems designed to perform tasks, make decisions, interact with users or respond automatically without human supervision. By combining data analysis, learning automation, and automation they deliver faster and more efficient results than human agents ever could alone. Simply stated: AI agents serve as digital assistants capable of thinking, acting and communicating on behalf of specific goals to reach a common objective.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents vary in complexity and use case. The main types include:
- Chatbots: Chatbots provide basic customer services via text or voice technology.
- Virtual assistants: Manage tasks such as scheduling meetings and setting reminders while also providing information.
- Autonomous agents: Automate complex, multi-step processes independently, such as managing workflows or analyzing large datasets.
Key Functionalities
Across their different forms, AI agents can:
- Understand and respond to natural language
- Real-time processing of large volumes of data.
- Learn from user interactions for improved accuracy.
- Automate repetitive or rule-based tasks
- Integrate with other software systems or APIs
Common Applications
AI agents are used across a wide range of industries, including:
- Healthcare: Managing appointments, patient queries, and diagnostics assistance
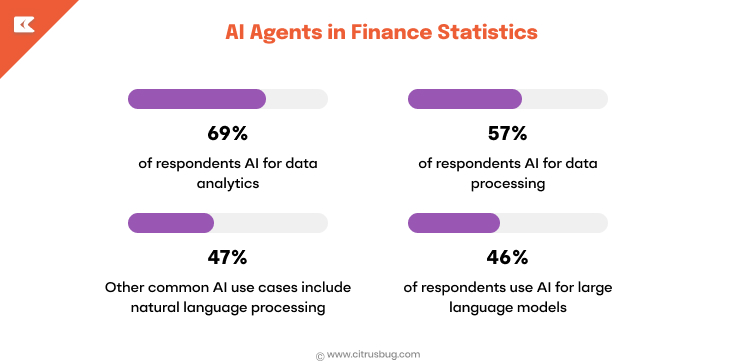
- Finance: Detecting fraud, automating support, and improving client communication
- E-commerce: Delivering personalized shopping experiences and customer service
- Logistics: Tracking shipments and optimizing supply chains
- Real estate: Streamlining property searches, client engagement, and documentation through AI agents in real estate
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents have evolved beyond being experimental tools; they now play a central role in how businesses and technology ecosystems function. With more companies actively adopting AI agents into their operations, we will examine statistics, trends, and market observations related to this emerging impact over the coming decade (2025-2035).
As reflected in recent AI Agents Statistics, organizations are increasingly relying on these systems not only to automate tasks but also to enhance decision-making, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
AI Agents Adoption Rates in 2025
AI agents are emerging as core to business automation and customer experience strategies across the globe. Companies shifted quickly for increased efficiency, scalability, and personalization, and subsequently momentum has continued. In fact, McKinsey recently reported that 72% of organizations worldwide have adopted at least one AI-based automation solution, AI agents are among the featured use cases.
Global Adoption Overview
- Enterprise adoption: Approximately 57% of large enterprises have utilized AI agents in recent years, deploying these agents for customer support, marketing, analytics, and other capabilities.
- Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs): Roughly 38% of small and midsized businesses (SMBs) already employ AI assistants or workflow automation tools for functions like customer service, marketing, recruitment etc. Their use is expected to accelerate over the coming years.
- Overall growth: The global AI agents market is projected to experience rapid year-on-year expansion from $5.4 billion in 2024 to $7.6 billion by 2025 due to advancements in natural language processing, increased automation demands, widespread cloud adoption for business use cases and reduced prices on AI agents for businesses.
Adoption by Region
North America: Leading the Charge
North America continues to dominate the global AI agents ecosystem. A recent survey by Deloitte indicates that 78% of organizations in North America plan to increase artificial intelligence investments in the upcoming fiscal year. This indicates a high-level commitment to AI adoption.
AI adoption rates have skyrocketed across the US in recent years, particularly Colorado and Washington D.C. where AI usage stands at 7.4% and 7.2% respectively.
Europe: Emphasizing Ethics and Compliance
A PwC survey indicates that 79% of companies have already adopted AI agents, and two-thirds report measurable value through increased productivity.
PwC’s survey indicates that 79% of businesses currently use artificial intelligence agents and two-thirds can quantify its benefits through increased productivity.
[Source]
Asia-Pacific: Rapid Growth and Ambitious Targets
The Asia-Pacific region has the fastest AI adoption. IDC anticipates that spending on AI in the region will reach $175B by 2028, driven by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 59.2% for Generative AI.
India will see AI adoption grow rapidly; 93% of business leaders plan on using artificial intelligence agents within 12-18 months according to Microsoft’s Work Trend Index 2025 Report.
Key Drivers of Adoption
- Automation efficiency: AI agents have shown to cut manual work and operational costs by at least 30 per cent while simultaneously increasing speed and productivity.
- Scalability and personalization: Businesses are turning to AI agents in order to automate tasks while providing real-time, personalized engagement for clients.
- AI maturity: No-code tools and platforms that offer AI chatbots have helped non-technical users access AI agents more easily than before.
AI agents statistics demonstrate that 2025 will mark a pivotal turning point for enterprise automation. Businesses of all regions and sizes are moving away from isolated use cases toward complex agent ecosystems utilizing automation as an enabler of growth and innovation.
Market Insights for AI Agents
This section summarizes current market size, growth projections, the competitive landscape, investment trends, and emerging platforms.
Current Market Size and Projected Growth
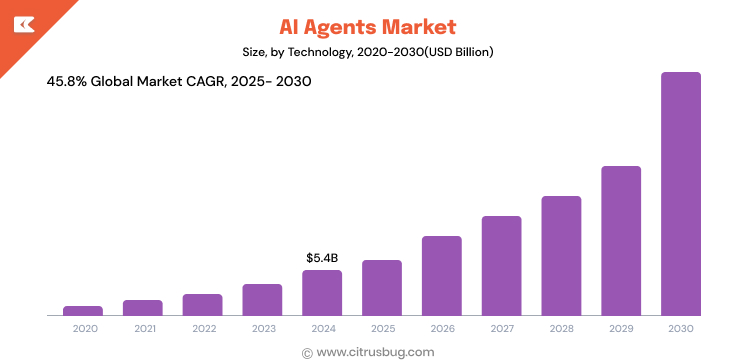
- Estimates of AI agents market are highly subjective to methodology used, yet all agree it will rapidly expand. MarketsandMarkets projects a market size for AI agents of USD 7.8 billion in 2025 with projected compound annual compound annual growth rates reaching 46.3% from then until 2030.
- Grand View Research estimates similar long-term market size projections, forecasting that artificial intelligence agents would reach USD 50.31 billion by 2030 with compound annual compounded annual growth at 45.8% over this time frame from 2025-2030.
What to take away: In the near-term (2024-2025), companies’ estimations of market size will differ due to scope; while long-term (2030) forecasts rely on consistent and rapid multibillion-dollar growth projections.
The Competitive Landscape
Leading technology firms such as OpenAI, Google, Microsoft and Anthropic are continually pushing the limits of AI agents with improved generative AI and conversational automation technology, driving wider acceptance worldwide, especially within areas like customer engagement analytics and process management.
At the same time, open-source frameworks such as LangChain, Hugging Face Transformers and AutoGPT have made developing AI agents simpler for smaller teams, thus expanding access to this technology to companies of any size previously only feasible for larger enterprises.
The Role of Specialized Developers
AI software development companies serve as essential partners, with domain expertise and customization services provided directly by them. Businesses increasingly look for tailored solutions which seamlessly align with their data, workflows, and compliance regulations.
Focusing on business-centric agent design, workflow automation and secure model integration allows these firms to bridge the gap between generalized AI platforms and enterprise needs in practice. This is particularly evident among industries using specialized agents, from AI agents in business operations such as business processes automation or real estate for property automation or client engagement.
Market Growth and Investment Trends
According to Precedence Research, the worldwide AI agents market is worth $5.43 billion USD in 2024 and is expected to reach $7.92 billion USD by 2025, expanding at an annual rate of over 40%. The acceleration is largely due to mounting investments from enterprises, a growing market for outsourced AI development services, and the increasing number of AI-as-a-Service platforms.
Major funding continues to flow toward AI automation startups and enterprise integration tools. The focus has shifted from experimental chatbots to developing AI chatbots capable of autonomous decision-making, predictive analytics, and adaptive learning — making AI agents more integral to long-term digital strategies.
Emerging AI Agent Platforms and Tools
The field of AI agent development is evolving quickly, with several noteworthy examples of AI agent platforms as well as new tools focused on helping businesses satisfy their requirements:
- Google Gemini Enterprise: Launched in October 2025, this platform allows businesses to create and deploy AI agents based on Google’s state-of-the-art Gemini models. This platform can create pre-built agents for more traditional tools, such as data analysis and, with a no code workbench, leverage those AI frameworks as customized agents and agents integrated with existing tools such as Google Workspace and Salesforce.
- Microsoft AutoGen v0.4: An enterprise-focused framework that has evolved to support complex multi-agent systems. The latest version introduces structured retrieval augmentation and Model Context Protocol (MCP) integration, enhancing performance and reducing deployment time.
- Salesforce Agentforce: Agentforce creates and manages AI agents in the Salesforce ecosystem, using Einstein AI while supporting both no-code and low-code agent generation approaches. So that anyone can use these tools.
- Lindy: Lindy is a no-code platform for non-technical teams and organizations to create AI agents designed to automate tasks and workflows and impose order to operational services.
These examples suggest that there are many different paths to the development of AI agents, agents that support varied organizational requirements for businesses and technical ability for teams.
Trends Shaping the Future of AI Agents
This section outlines the main trends shaping AI agents and the evidence behind them. Short paragraphs and bullet lists improve scanability. Key data points and sources are provided for credibility. Building on these AI agents statistics and recent AI development stats, several key trends are shaping how organizations will design and deploy intelligent agents in the near future.
Integration with Generative AI and Advanced NLP
- Generative models and improved natural language processing are enhancing agents’ ability to understand and generate complex responses in a rich context with intention. The result of this change is a shift away from strictly scripted responses and toward more task-based, contextual interactions.
- Vendors and enterprises are embedding generation and retrieval methods into agents to produce on-demand summaries, drafts, and decision-making processes. As a result, agent workflows are increasingly combining a foundation model, retrieval augmented generation (RAG), and domain connectors.
AI Agents in Personalized Customer Experiences
- Consumer expectations are driving personalization: Surveys show approximately 71% of customers expect to experience some personalized situation from companies, and many experience frustration when personalization is missing. Agents that have access to user data and context provide the personalization we seek.
- When agents enable personalization, acquisition and retention costs can decline while conversion increases, assuming we do it right; organizations already invest in agent functions that allow for segmentation, dynamic messaging, and real-time recommendations.
Increased Adoption of Autonomous Decision-Making Agents
- Organizations are now piloting semi-autonomous and fully autonomous agents that can initiate actions, manage workflows, and make decisions based on data with set guardrails.
- In a 2025 EY survey, 48% of technology executives indicated they have either adopted or are fully deploying agentic AI to manage repetitive operations, or engage customer interactions. Deloitte further adds that about 25% of organizations that are currently using generative AI, will deploy agentic AI proofs of concept in 2025.
- Adopting AI technology presents challenges. A study revealed that while 79% of organizations had implemented AI agents, only 66% reported tangible productivity increases as evidence of improved evaluation metrics and business alignment.
Ethical AI, Data Privacy, and Regulatory Considerations
- With AI agents becoming more autonomous, ethics and data privacy are becoming ever more relevant issues. Regulators have begun raising concerns over how AI systems use data when making their determinations.
- The World Economic Forum (2025) reported that global trust in AI companies declined 12% year-on-year, due to users raising issues over unclear data use policies and fairness concerns. Furthermore, only 25% of organizations currently possess an established AI governance framework in place.
- As regulators across Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific introduce AI governance laws, businesses must invest in auditability, explainability, and access control systems to maintain customer confidence while remaining compliant and maintaining customer trust.
Investment and Budget Trends Enabling These Shifts
- Enterprises are dramatically increasing budgets for AI agents and the supporting infrastructure. According to TechMonitor (2025), 88% of U.S. firms plan to increase AI spending within the next 12 months. AI agents have also been noted as a top investment area for firms.
- This investment demonstrates how agentic systems have transitioned from experimental infrastructure into core operational infrastructure.
Predictions for 2026 and Beyond (What to watch)
- Over time, agents-enabled workflows should expand across HR, finance, logistics and customer service departments. As organizations adopt these technologies, partnering with a system integrator ensures smooth deployment and interoperability between existing enterprise systems. Gartner projects that by 2028 approximately 33% of enterprise software applications will have agentic AI capabilities compared with only less than 1% back in 2024, showing just how rapidly agentic AI technologies have become integral parts of enterprise systems.
- The next phase will likely bring a period of consolidation: vendors that can deliver governance, observability, and accuracy will lead, while pilot projects without measurable ROI may decline.
- Trust, governance, and transparency will determine which agent use cases scale fastest. Organizations combining technical sophistication with strong oversight and clear KPIs will be best positioned to expand AI agent responsibilities responsibly.
These trends show how technological advances, business priorities, and social expectations are converging around AI agents. Use AI agents statistics and governance indicators to guide which agent projects to prioritize and how to measure success going forward.
Challenges and Considerations
Employing AI agents allows for definite benefits, and organizations are faced with various hurdles that can affect implementation, security, and readiness of the workforce. Understanding these challenges allows organizations to better plan and avoid costly pitfalls.
Implementation Hurdles
- Technical complexity: Integrating AI agents with existing systems, databases, and APIs can be complicated. Ensuring interoperability across legacy software, cloud services, and multiple departments often requires significant engineering effort.
- Budget constraints: Funding for an AI agent is more than just the purchase of the tool, there are also infrastructures, licensing, and on-going maintenance. Many organizations quote budget uncertainty for variable reporting of AI adoption.
- Cultural resistance: Workforce concerns about AI replacing or altering jobs are common. For example, in India, a study of white-collar workers found 60% believe AI will automate their job in the next five years, and 48% believe it already replaces roles in their industry.
Security, Compliance & Governance Challenges
- Governance gaps: Even in sectors where AI is seen as mission-critical, governance is often lagging. A Corporate Compliance Insights survey of financial services firms reported nearly 80% see AI as essential, but only 32% have formal AI governance programs established.
This governance gap introduces regulatory, ethical, and operational risk as AI agents take on more and more of the responsibility. - Risk & data protection: Agents frequently work with sensitive data. This leads to queries related to access control, audit logs, explainability, and protection against unintentional data leaks or misuse. As agents gain more independence, these risks become more real.
Skills and Talent Gaps
- Workers express anxiety both around job security and being unprepared. The study of white-collar workers in India illustrates that many workers believe that AI will be a major contributor to automation (60%) and already replace jobs in their industry (48%).
- Finding people with expertise in architecture and development, maintenance, and governance for AI agents is still a major challenge in organizations. In many instances, the default plan is to outsource development when there isn’t internal talent.
Key Takeaways & Conclusion
AI agents are revolutionizing how businesses run, from automating mundane tasks to improving customer experiences. Their applications span industries like finance, healthcare, logistics and retail; becoming part of daily workflows across these fields as they revolutionize operations such as real estate transactions or developing chatbots that save organizations time while improving accuracy and making smarter decisions.
Businesses looking at artificial intelligence agents should focus on starting strategically, prioritizing high-impact use cases, planning integration, governance and talent needs and keeping informed with emerging platforms and trends, while being mindful in adopting AI solutions internally or via outsourcing AI development services, so as to unlock efficiency, scale operations efficiently, maintain their edge competitive edge within an ever-evolved digital landscape.




 SaaS Development
SaaS Development Web Application Development
Web Application Development Mobile Application Development
Mobile Application Development Custom Software Development
Custom Software Development Cloud Development
Cloud Development DevOps Development
DevOps Development MVP Development
MVP Development Digital Product Development
Digital Product Development Hire Chatbot Developers
Hire Chatbot Developers Hire Python Developers
Hire Python Developers Hire Django Developers
Hire Django Developers Hire ReactJS Developers
Hire ReactJS Developers Hire AngularJS Developers
Hire AngularJS Developers Hire VueJS Developers
Hire VueJS Developers Hire Full Stack Developers
Hire Full Stack Developers Hire Back End Developers
Hire Back End Developers Hire Front End Developers
Hire Front End Developers AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting
AI Healthcare Software Development & Consulting Healthcare App Development
Healthcare App Development EHR Software Development
EHR Software Development Healthcare AI Chatbot Development
Healthcare AI Chatbot Development Telemedicine App Development Company
Telemedicine App Development Company Medical Billing Software Development
Medical Billing Software Development Fitness App Development
Fitness App Development RPM Software Development
RPM Software Development Medicine Delivery App Development
Medicine Delivery App Development Medical Device Software Development
Medical Device Software Development Patient Engagement Software Solutions
Patient Engagement Software Solutions Mental Health App Development
Mental Health App Development Healthcare IT Consulting
Healthcare IT Consulting Healthcare CRM Software Development
Healthcare CRM Software Development Healthcare IT Managed Services
Healthcare IT Managed Services Healthcare Software Testing services
Healthcare Software Testing services Medical Practice Management Software
Medical Practice Management Software Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services
Outsourcing Healthcare IT Services IoT Solutions for Healthcare
IoT Solutions for Healthcare Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services
Medical Image Analysis Software Development Services Lending Software Development Services
Lending Software Development Services Payment Gateway Software Development
Payment Gateway Software Development Accounting Software Development
Accounting Software Development AI-Driven Banking App Development
AI-Driven Banking App Development Insurance Software Development
Insurance Software Development Finance Software Development
Finance Software Development Loan Management Software Development
Loan Management Software Development Decentralized Finance Development Services
Decentralized Finance Development Services eWallet App Development
eWallet App Development Payment App Development
Payment App Development Money Transfer App Development
Money Transfer App Development Mortgage Software Development
Mortgage Software Development Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development
Insurance Fraud Detection Software Development Wealth Management Software Development
Wealth Management Software Development Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development
Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Development Neobank App Development
Neobank App Development Stock Trading App Development
Stock Trading App Development AML software Development
AML software Development Web3 Wallet Development
Web3 Wallet Development Robo-Advisor App Development
Robo-Advisor App Development Supply Chain Management Software Development
Supply Chain Management Software Development Fleet Management Software Development
Fleet Management Software Development Warehouse Management Software Development
Warehouse Management Software Development LMS Development
LMS Development Education App Development
Education App Development Inventory Management Software Development
Inventory Management Software Development Property Management Software Development
Property Management Software Development Real Estate CRM Software Development
Real Estate CRM Software Development Real Estate Document Management Software
Real Estate Document Management Software Construction App Development
Construction App Development Construction ERP Software Development
Construction ERP Software Development