Medical imaging software plays an integral part in the modern world of healthcare. It is the engine behind the instruments that allow clinicians to see inside the human body, identify the most accurate diagnosis, and guide treatment with confidence. As digital transformation accelerates in medicine, medical imaging software development has become a significant investment opportunity for diagnostic centers, hospitals, and healthcare technology teams.
The demand for more advanced imaging capabilities and integration of artificial intelligence and more efficient workflows for clinical care are transforming the way imaging equipment is designed and used. Healthcare facilities are looking to find software that not just handles large amounts of imaging data but also ensures speed, accuracy, and interoperability across different care environments.
For healthcare professionals looking to develop custom imaging solutions, understanding the medical imaging software development process can help distinguish between software that functions and software that enhances diagnostic precision and operational outcomes. In this article we explain the process of developing software for medical imaging, what it includes, the places it is employed, the techniques that underlie it, and the best ways to create systems that are efficient and scalable. They are also aligned to the clinical requirements.
What Is Medical Imaging Software Development?
Medical imaging software development involves creating software that can process, collect and manage medical images from devices such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs and ultrasounds. The aim is to provide healthcare professionals with precise information while making sure that patients are safe and in compliance with standards for healthcare.
This type of development incorporates medical expertise, software engineering, and AI. The solutions that are customized to every provider, helping to enhance workflow, facilitate real-time diagnostics, or incorporate AI for improved image analysis. In contrast to generic devices, these systems are designed to address specific medical needs and integrate seamlessly with the hospital infrastructure.
Interoperability is another important aspect. Modern systems integrate with PACS and EHR platforms and adhere to DICOM standards, ensuring secure and effective sharing of pictures and the patient’s information. In simple terms, medical imaging software development involves the creation of platforms that increase the accuracy of diagnosis and streamline workflows in clinical practice and enhance the patient experience.
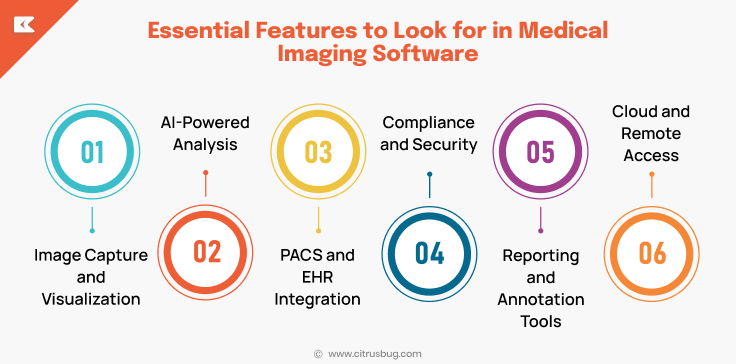
Essential Features to Look for in Medical Imaging Software
The right choice for medical imaging software is about paying attention to features that increase the accuracy of diagnostics as well as workflow efficiency and regulatory conformity. Here are the top features:
Image Capture and Visualization
It supports multiple imaging techniques, including MRI, CT, X-ray, and ultrasound. High-resolution images are available with tools for panning, zooming, and multi-planar viewing that allow clinicians to examine the details more efficiently.
AI-Powered Analysis
Artificial Intelligence is used to automate the detection, segmentation and classification of irregularities. Aids radiologists in saving time, cutting down on mistakes, and increasing confidence in diagnosis.
PACS and EHR Integration
The seamless integration with PACS, EHR, and hospital management systems makes sure that patient information and imaging records are readily accessible. This improves workflows and decreases duplication of work.
Compliance and Security
The system includes HIPAA, FDA, and DICOM compliance as well as data encryption and access control based on role. It ensures that patient information is secured and the system is compliant with the requirements of regulatory agencies.
Reporting and Annotation Tools
Clinicians can add notes or measurements as well as detailed reports directly onto images. It facilitates collaboration, documentation, and communication between care teams.
Cloud and Remote Access
Supports the use of telemedicine and multi-site collaboration in addition to scalable cloud storage. Large imaging data sets can be accessed from any location while ensuring security and performance.
Where Medical Imaging Software Is Used Across Healthcare Settings
Medical imaging software is an indispensable tool in numerous healthcare environments:
Hospitals and Radiology Departments: The equipment is used to collect, store and analyse CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays, as well as ultrasounds. Help radiologists by providing precise and quick identification of ailments.
Speciality Clinics: Cardiology, oncology, and orthopaedic teams utilize imaging software to monitor how well treatments are done with precision.
Teleradiology Services: Enables sharing of images among clinics and remote specialists, facilitating the delivery of high-quality treatment.
Research and Clinical Trials: Provides an image capture and analysis system that is simple to standardize, which allows scientific research that is based on data and medical breakthroughs.
Medical imaging software is not only a tool. It is a platform to improve the clinical workflow, improve the accuracy of diagnosis, and facilitate better outcomes for patients.
Key Technologies Used in Medical Imaging Software Development
Medical imaging software relies on a combination of advanced technologies to capture, process, analyze, and manage medical images effectively. These technologies ensure accuracy, interoperability, and clinical usability.
Image Processing and 3D/4D Reconstruction
The algorithms work with raw MRI, CT, ultrasound, and X-ray images. They improve clarity, reduce noise, and can also reconstruct 3D or 4D images, thereby achieving real-time viewing. This is crucial to surgical planning, oncology,y and interventional work.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI models identify patterns, categorize anomalies, and help in real-time diagnostics. The system uses machine learning to become more accurate with time by analyzing large volumes of data. AI is what empowers predictive analytics and decision-making processes.
Image Segmentation and Annotation
Segmentation tools can highlight specific organs, lesions, or areas of particular interest. Annotation tools enable radiologists as well as AI models to define and study important areas, increasing the accuracy of diagnostics and training data for AI.
PACS and DICOM Integration
The integration in PACS (Picture Communications and Archiving Systems) and compliance with DICOM standards guarantee secure storage and efficient sharing of images. These systems allow the seamless integration of EHRs as well as other platforms for healthcare.
Visualization and Reporting Tools
Advanced visualisation dashboards, multiplanar reconstructions (MPR) and automated reports help doctors interpret images swiftly and accurately. These tools help standardize outputs and facilitate collaboration in care.
Cloud and On-Premise Deployment
The most up-to-date software is now available as cloud-based software to help you scale your company, as well as on-premise for high security. The choice of deployment is contingent on the hospital’s infrastructure, compliance, and the requirements for performance.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection
Medical imaging software should secure sensitive patient information. Access based on role, encryption, and adherence to HIPAA, FDA, and other regulations are crucial. Secure handling is a guarantee of confidence and reliability in clinical care.
Data Analytics and Decision Support
Analytics modules analyze patterns and trends across the patient’s imaging data. Together with AI analytics, these tools provide insight that helps determine outcomes, improve workflows, and help support medical decisions based on evidence.
Medical Imaging Software Development Process
Developing medical imaging software takes several steps to ensure that it is reliable, accurate, and compliant with health standards. Each step is essential in delivering software that enhances diagnosis workflows and the outcomes of patients.
Requirements Gathering and Clinical Validation
The process begins with knowing the needs of patients as well as hospital processes. Teams work with radiologists, technicians, and IT personnel to determine specific features, imaging techniques, and integration needs. Early validation ensures that the software matches the needs of real-world healthcare.
Software Design and UI/UX
Design is focused on providing intuitive interfaces for clinicians and radiologists. Easy navigation, clear visualization, and custom dashboards improve efficiency. Design that is based on workflows reduces the chance of errors and facilitates easy adoption.
Development and AI Model Training
Developers create core functions like image storage, processing and AI-based analyses. Machine learning models are trained on annotated datasets to identify irregularities and evolve over time. Integration with the PACS and EHR system is in process at this time.
Testing and Compliance Checks
Software is tested rigorously to ensure accuracy and performance as well as security. Conformity to HIPAA, FDA, and DICOM standards is checked. Any issues are resolved prior to deployment to ensure the safety and reliability.
Deployment and Integration
After validation, the software is deployed in hospitals either on-site or on the cloud. Integration with the existing infrastructure will ensure smooth workflows as well as secure sharing of images. Training is given to staff members to facilitate the adoption.
Ongoing Maintenance and Optimization
Medical imaging software requires constant updates to ensure accuracy, security and performance. AI models are retrained every time as more data becomes available, and the latest imaging technology is integrated to keep the system current.
Key Challenges in Medical Imaging Software Development
Making medical imaging software is an intricate process. It involves balancing clinical accuracy, technical performance, and the requirements of regulatory. Below are some of the most frequently encountered issues that healthcare organizations and development teams confront.
Data Quality and Annotation
Medical imaging AI relies on well-organized, high-quality datasets. But the data for imaging often is derived from a variety of formats, devices and environments for clinical use. Inconsistent labelling or poor image quality could affect the accuracy of models and their reliability.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many hospitals still use outdated PACS or imaging systems. The integration of new software into such systems may be challenging. Problems with compatibility and data silos, as well as interruptions in workflow, are typical issues when implementing.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Medical imaging software must comply with strict regulations in the field of healthcare. Data privacy laws, such as HIPAA, and clinical safety standards, like FDA guidelines, can add complexity to the process. Ensuring compliance throughout the software lifecycle involves careful planning, documentation, and validation.
Accuracy, Bias, and Clinical Validation
AI-driven imaging systems have to produce consistent and easily explainable results. Training data that is biased or a lack of clinical validation could lead to incorrect results. This can cause trust issues between healthcare professionals and limit real-world adoption.
Performance and Scalability
Imaging software needs to handle huge file sizes and large quantities of data with no delay. Insufficient performance could affect the speed of diagnosis as well as workflows in clinical practice. In addition, the process of scaling the system across facilities or departments can add another dimension of complexity.
Cloud vs On-Premise Medical Imaging Software
When deploying medical imaging software, hospitals and clinics must decide between cloud-based or on-premise solutions. Each approach has advantages and trade-offs, depending on infrastructure, data privacy, and performance requirements.
| Feature / Factor | Cloud-Based Deployment | On-Premise Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Data Security | Requires robust encryption and compliance management. Data is stored off-site. | Full control over data and infrastructure. Ideal for strict privacy policies. |
| Scalability | Easily scales with growing imaging volumes and multi-site needs. | Scaling may require additional servers and hardware investments. |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs with a subscription-based pricing model. | Higher initial investment for servers, maintenance, and IT resources. |
| Accessibility | Remote access enables telehealth and teleradiology services. | Access is typically limited to the local network unless additional setup is implemented. |
| Maintenance | Updates, backups, and system maintenance are managed by the provider. | Requires an in-house IT team for maintenance and software updates. |
| Performance | Performance depends on internet speed and may experience latency with large image files. | High local performance with faster access to large datasets. |
Cost of Medical Imaging Software Development
The cost of developing medical imaging software varies widely depending on complexity, features, and compliance requirements. Hospitals and healthcare providers should consider multiple factors before budgeting. Here’s a typical breakdown:
| Component / Factor | Estimated Cost Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Image Processing Module | 30,000 – 80,000 | Core image capture, storage, and viewing functionality |
| AI and Machine Learning Integration | 50,000 – 150,000 | Includes anomaly detection, predictive analytics, and training datasets |
| PACS / EHR Integration | 15,000 – 50,000 | Custom connectors and interoperability with hospital systems |
| Compliance & Regulatory Validation | 20,000 – 60,000 | HIPAA, FDA, DICOM, and clinical validation requirements |
| 3D/4D Reconstruction & Visualization | 15,000 – 50,000 | Advanced visualization and multiplanar reconstructions |
| Deployment & Infrastructure | 10,000 – 30,000 | Cloud setup or on-premise hardware costs |
| Maintenance & Updates (Annual) | 10,000 – 30,000 | Security patches, AI retraining, and software updates |
| Total Estimated Cost | 150,000 – 500,000 | Depends on project complexity, AI modules, and compliance requirements |
How to Choose the Right Medical Imaging Software Development Company
The selection of the best partner for development is crucial to creating efficient, compliant, and secure healthcare imaging programs. A reliable company will ensure that the project is completed on time, within budget, and also meets the needs of your patients. Here are a few things to think about:
Expertise in Healthcare and Imaging
Choose a company that has demonstrated expertise in healthcare software development and medical imaging, specifically. Find a company with proficiency in PACS connectivity, AI models, and DICOM standards, as well as integration with EHRs.
Regulatory Knowledge and Compliance
Your partner should be aware of the HIPAA compliance checklist, the FDA, and other regulations in the region. The compliance should be incorporated into the process of development, including documentation as well as testing and validation.
Custom Development Capabilities
Every clinic or hospital has its own workflow. A software development company must offer bespoke solutions instead of generic software. It is important to ensure that features meet the clinical and operational needs of your organization.
Transparent Development Process
A trustworthy partner will give clearly defined timelines and milestones for projects as well as regular updates. Continuous feedback and agile development loops can help identify issues early and enhance the quality of the product.
Post-Deployment Support
Medical imaging software requires continuous maintenance, updates and AI model training. Make sure your developer partner provides long-term support for upgrades as well as security patches and changes in clinical requirements.
Reviews, Case Studies, and Client Feedback
Check the client testimonials on Clutch and previous work. Case studies and reviews provide insight into their delivery quality, technical expertise, and ability to meet healthcare compliance standards.
Future Trends in Medical Imaging Software Development
Medical imaging software is evolving fast. New technologies, clinical demands, and emerging healthcare trends are shaping the next generation of diagnostic tools.
Rapid Growth of AI in Imaging
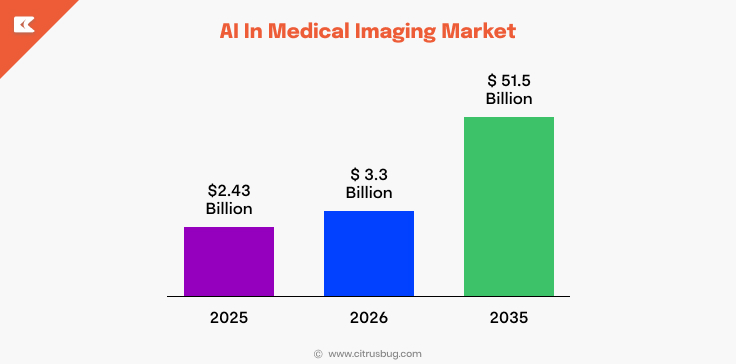
AI adoption in medical imaging is accelerating. The global AI in medical imaging market was valued at around USD 2.43 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow to over USD 28.01 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of more than 35.71% from 2025 to 2033. This growth reflects hospitals using AI for faster results, improved image interpretation, and workflow automation.
Growing Market Share and Adoption
The AI in the medical imaging market is growing rapidly. In 2025, North America led with a 40.6% market share, reflecting strong adoption of AI-powered imaging solutions. Hospitals are increasingly using these tools to improve diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency.
Interoperability Takes Priority
Future medical imaging platforms will place even greater emphasis on standards such as DICOM, HL7, and FHIR. Strong interoperability ensures images and associated data flow securely between PACS, EHRs, and decision support tools, reducing manual steps and the risk of errors.
Cloud, Edge, and Hybrid Architectures
Cloud platforms expand storage and remote collaboration, while edge computing helps process imaging data close to where it’s generated, reducing latency. Hybrid deployment models are becoming common in larger hospital networks to balance performance and security.
Personalized and Predictive Diagnostics
Advanced imaging software is integrating with analytics to support predictive insights. This enables early intervention and tailored patient care, especially in oncology and cardiology.
Conclusion: Building Reliable and Compliant Medical Imaging Software
Medical imaging software development is vital for healthcare professionals seeking to improve the accuracy of diagnostics and speed up clinical workflows. Based on specific clinical requirements, they can manage the complex imaging data, seamlessly integrate with the existing hospital infrastructure and help in quicker, more informed decision-making.
At Citrusbug, we design and develop custom imaging solutions to complement our greater experience in healthcare software development. Our goal is to deliver secure, scalable and compliant software that can adapt to changing medical requirements while also aiding the long-term digital health initiative.