AI systems are no longer limited to static models or one-time predictions. Today, they can observe their environment, make decisions, and take action with minimal human input. These capabilities come from AI agents, which now form the foundation of intelligent and autonomous software systems across industries.
With the organizations continuing to drive towards the digital transformation, understanding the types of AI agents becomes increasingly important. Different agent models facilitate automation, decision-making, and optimization in areas such as finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing. According to McKinsey, 72% of all organizations across the globe have implemented at least one AI-based automation solution, which indicates the increased dependence on systems capable of responding and evolving in real time.
This guide describes how AI agents work, the different models used in practice, and where they are applied in real-world scenarios. We begin with the fundamentals before exploring more advanced agent architectures and use cases.
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is an intelligent system that can perceive its environment, process information, and take actions to achieve a specific goal. Unlike traditional software, an AI agent does not follow a fixed script. Instead, it responds to inputs, measures results, and alters its behaviour with time.
In artificial intelligence, the agents are characterized by the way they communicate with their surroundings. They take data from sensors or other inputs. Then they apply decision logic. Finally, they do it in the form of recommendations, predictions, or automated actions. This is the perception-decision-action loop that makes AI agents different from standalone AI models.
From a practical standpoint, AI agents in the business are usually integrated into bigger systems. They can track transactions or optimize workflows, or assist in real-time decision-making. The intelligence of an agent is determined by its design. Some agents follow simple rules. Others use learning mechanisms to improve with experience. It is important to understand this distinction before discussing the various categories of AI agents and their applications in systems in the real world.
Let’s now look at how AI agents actually work under the hood, starting with their core architecture and decision flow.
How AI Agents Work: Architecture and Decision Flow
AI agents operate through a structured flow of perception, decision-making, and action. At the centre, they continually scan their surroundings, analyze information and perform actions to get towards predetermined objectives. This cycle enables them to respond and adapt to changes on a real-time basis.
Core Components of an AI Agent
- Perception Layer: Agents gather data from their environment through sensors, APIs, or user inputs. It can be structured, such as the records of transactions, or unstructured, such as text or images. Proper perception guarantees the agent acts on informed decisions.
- Decision-Making Engine: The agent processes the data based on rules, models, or learning algorithms. This can be in the form of simple condition-action rules, goal-oriented planning, or advanced reinforcement learning models, depending on the type of agent. The decision engine defines how the agent chooses the best action to achieve its objectives.
- Action Execution: After making a decision, the agent takes action. This can be an automatic program update, sending a suggestion to a user, raising an alarm, or changing the operational parameters. The effectiveness of the agent depends on timely and accurate execution.
- Learning and Feedback Loop: Advanced AI agents use feedback of past activity to enhance future performance. Learning can be a process of modifying internal models, revising policies, or improving predictions. In the long run, this helps agents to optimize their performance and work with increased autonomy.
Interaction with the Environment
Not every AI agent works in the same way. Some operate under fully observable settings, and all the relevant information is accessible. Others have to make decisions using incomplete information in a partially observable environment. Agents can operate independently (single-agent systems) or collaborate with others (Multi-agent systems) to solve complex problems such as supply chain optimization or autonomous fleet management.
It is essential to understand this architecture before delving into the types of AI agents, as the way an agent perceives, decides and acts is a major factor in determining the best model to use in a specific application. Next, we will discuss these types and where each of them excels in practical applications.
Different Types of AI Agents
The AI agents can be categorized according to the way they observe their environments, make decisions and perform actions to reach the desired objectives. Understanding these types helps engineers, architects, and decision-makers select the right agent for their specific needs.
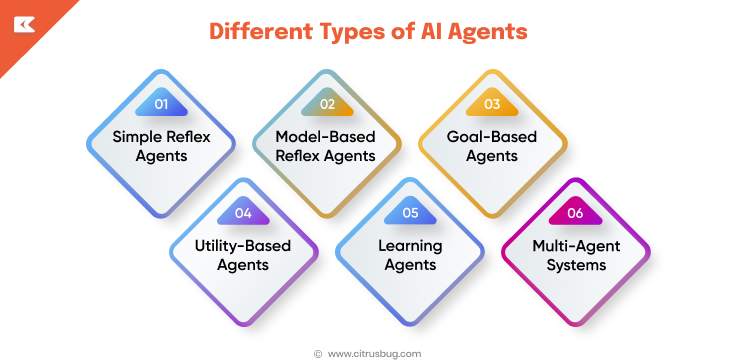
1. Simple Reflex Agents
These agents operate on a condition-action basis. They react to certain inputs by instituting actions, without taking into consideration the past experiences or the future repercussions. Although quick and effective, they cannot work well in dynamic or unpredictable places. They are most suited to simple tasks where the environment is stable and predictable.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
Model-based agents maintain an internal state representing aspects of the environment. This enables them to make informed decisions even when not everything can be seen at once. They are capable of dealing with more complex situations than simple reflex agents by tracking what happened in the past. They come in handy, especially when there is incomplete information about the environment and prior context needs to be integrated with the current information to make decisions.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents make decisions to achieve specific objectives rather than simply reacting to inputs. They consider various actions that can be taken and identify those that are likely to achieve the intended result. This strategy enables them to think ahead and act on what matters according to the goals and not the rules alone. They work well in situations where long-term planning and versatility are significant.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents quantify the desirability of different outcomes. They make decisions that maximize total utility, including considerations such as cost, performance, and risk. In contrast to goal-based agents, utility-based agents may contrast competing objectives and make a decision regarding the most preferable trade-offs. They are appropriate in a situation where multiple goals have to be addressed at the same time.
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents improve their performance over time by adapting to new data and feedback. They improve on their decision-making strategies depending on experience, which makes them cope with dynamic, changing environments. The learning agents prove useful in scenarios where the system needs to adapt to its surroundings or refine its behavior through repeated experiments.
6. Multi-Agent Systems
In multi-agent systems, multiple agents coordinate and collaborate to solve complex problems that a single agent cannot handle alone. This involves communicating, negotiating, and mutual decision-making. Multi-agent systems are especially useful in large-scale or distributed systems where duties have to be shared by multiple agents and coordinated effectively to achieve efficiency and reliability.
Diffrent Types of AI Agents Across Industries
AI agents are transforming industries by automating decisions, improving efficiency, and enabling smarter interactions across complex systems. From healthcare and finance to manufacturing and retail, different types of AI agents are designed to solve domain-specific challenges effectively.
Finance and Banking
AI agents assist financial institutions in making faster and data-driven decisions and decreasing risks. They are essential in terms of trading, fraud detection and risk management.
- Goal-Based & Utility-Based Agents: Optimize portfolio management and trading strategy.
- Learning Agents: Identify fraud through monitoring patterns over time.
- Multi-Agent Systems: Coordinate risk assessments and trading operations in real time.
Healthcare
AI agents are used in healthcare to improve patient care, diagnostics, and hospital functions. They enable the staff to concentrate on high-value activities as agents handle data-driven decisions.
- Model-Based & Learning Agents: Process patient data to detect health risks.
- Goal-Based Agents: Optimize the scheduling and resource allocation.
- Multi-Agent Systems: Make cross-departmental coordination to enhance patient flow.
Retail and E-Commerce
Retail operations are smoother and more personalized as AI agents assist in customer experience, inventory management, and supply chain optimization.
- Utility-Based Agents: Minimise prices, advertising and inventory.
- Learning Agents: Enhance personal recommendations in the long term.
- Goal-Based Agents: Plan and control deliveries and logistics effectively.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
AI agents are used for predictive maintenance, production planning, and logistics in factories, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
- Learning Agents: Identify anomalies and anticipate equipment failures.
- Goal-Based Agents: Optimize production schedules and workflows.
- Multi-Agent Systems: Coordinate distribution networks and inventory management.
Customer Experience and NLP
AI agents improve conversation-based interfaces and customer support using natural language processing(NLP), providing fast and context-sensitive answers.
- Learning Agents: Refine chatbot and voice assistant reactions with time.
- Goal-Based Agents: Process complex workflows like bookings and troubleshooting.
- Multi-Agent Systems: Aid in the smooth communication with various services simultaneously.
Reactive vs Deliberative AI Agents
AI agents can be broadly categorized based on how they make decisions: reactive or deliberative. Each types have its own advantages, weaknesses, and application to business requirements.
| Feature | Reactive Agents | Deliberative Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Approach | Immediate, rule-based decisions that react only to current inputs | Planned, model-based approach that evaluates multiple possible actions and outcomes |
| Environment Suitability | Fully observable and predictable environments | Partially observable or dynamic environments |
| Complexity | Simple to implement | More complex due to planning and modeling |
| Adaptability | Low adaptability; does not learn from past actions | High adaptability with the ability to incorporate feedback and adapt strategies |
| Use Cases | Alerts, monitoring systems, and basic automation tasks | Workflow optimization, predictive maintenance, complex scheduling, and multi-agent coordination |
Summary:
- Reactive agents are quick, straightforward and suited to the environment where rules and conditions are known.
- Deliberative agents are highly effective in planning, foresight, and decision-making in complex, changeable environments.
Tradeoffs When Choosing AI Agent Types
Choosing the right AI agent involves a balance between performance, complexity, and adaptability. Each type has advantages and limitations that make it suitable for specific tasks and environments. Some of the main tradeoffs are summarized in the table below:
| Agent Type | Strengths | Limitations | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Reflex Agents | Fast, easy to implement, with minimal resources required | Cannot handle complex or changing environments | Basic monitoring, alert triggers, and repetitive tasks |
| Model-Based Reflex Agents | Handles partially observable environments and maintains internal state | Limited planning capability and may struggle with highly dynamic tasks | Context-aware monitoring and intermediate automation tasks |
| Goal-Based Agents | Plans actions to achieve objectives and remains flexible and adaptive | Requires more computation and design, leading to slower decision-making | Workflow optimization, logistics planning, and strategic decision-making |
| Utility-Based Agents | Evaluates multiple outcomes and can optimize trade-offs | Complex to model and requires accurate utility functions | Resource allocation, financial modeling, and multi-objective optimization |
| Learning Agents | Improves over time by adapting to new data and feedback | Training can be time-consuming and may require large datasets | Predictive analytics, recommendation systems, and adaptive automation |
| Multi-Agent Systems | Solves complex distributed problems and enables collaboration | Coordination overhead and the need for communication protocols | Supply chain optimization, fleet management, and large-scale automation |
Key Considerations:
Complexity vs Speed: Simple agents are quick but limited; deliberative or learning agents are more intelligent, but slower in decision-making.
Adaptability: Learning and multi-agent systems are much more effective in dynamic settings, whilst reflex agents perform more effectively on predictable and stable tasks.
Resource Requirements: Advanced agents demand computing resources, information and detailed design, yet they can provide better ROI in complicated situations.
How Citrusbug Designs AI Agents
At Citrusbug, we provide AI development services, and we specialize in creating custom AI agents that meet business goals and operational needs directly. Instead of generic platforms, we focus on flexibility, scalability, and real-world performance.
Understanding Business Goals
We collaborate closely with stakeholders before the development process to understand specific objectives, workflows, and pain points. This makes sure that every AI agent is designed to provide measurable results, be it by automating decision-making, optimizing operations, or improving customer experiences.
Choosing the Right Agent Type
Not every AI agent can be used in every situation. Our team assesses whether a reactive, deliberative, learning, utility-based, or multi-agent system is best suited to address the needs of the client. The decision is based on factors such as the complexity of the environment, the needs of the decision-making process, or the autonomy necessary.
Designing Robust Architecture
We model AI agents in a clear perception-decision-action loop, combining data ingestion, decision-making models, and action execution. Advanced agents also encompass feedback and learning systems to enhance performance over time. It has a modular architecture, which is easy to update, scale, and integrate with existing systems.
Iterative Development and Testing
Our development process is iterative, combining agile methodologies with rigorous testing. We test agent behavior in real-life conditions to test reliability, accuracy, and responsiveness. This strategy minimises risks and makes agents work well in dynamic environments.
Continuous Optimization
We offer continuous monitoring and optimization after deployment. The AI agents are optimized on the basis of performance, dynamic data, and business objectives. This guarantees efficiency, flexibility and ROI in the long term.
By applying this method, businesses can leverage the capabilities of custom AI agents and reach their full potential, attaining automation, intelligent decision-making, and quantifiable operational enhancements.
Conclusion
AI agent trends are changing the way businesses are conducted as they are facilitating smarter decision-making, automation, and operational efficiency in any industry. From simple reflex agents to multi-agent systems, each type has its own advantages and tradeoffs based on the complexity of the tasks and the environment. Understanding these types is critical to an organization aiming to adopt effective AI solutions.
At Citrusbug, we offer outsourcing AI development solutions to create custom AI agents that fit your workflows, data, and goals. Our experience guarantees scalable, adaptive, and high-performing AI systems that lead to quantifiable outcomes. Collaborating with us can enable businesses to capitalize on the full potential of AI, streamline operations, and outcompete competition in the market.
FAQs on Types of AI Agents
What is the difference between AI agents, chatbots, and AI assistants?
- AI Agents: Intelligent systems that perceive, make decisions and take actions to achieve goals.
- Chatbots: AI agents specializing in text-based communication with users.
- AI Assistants: More advanced chatbots with capabilities to schedule, remind and recommend.
In short, every chatbot and AI assistant is an AI agent, but not every AI agent is a chatbot or an assistant.
What is the difference between reactive and deliberative AI agents?
The reactive agents react directly to the current inputs without planning, whereas deliberative agents have an internal view of the environment and make decisions to accomplish long-term goals. Reactive agents are faster in speed when deliberative agents suit complicated decision-making.
Where are AI agents used in real life?
AI agents find applications in many industries: finance (fraud detection, trading), healthcare (diagnostics, scheduling), retail (recommendations, logistics), manufacturing (predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization), customer service (chatbots, voice assistants) and more.
Should businesses use prebuilt AI platforms or custom AI agents?
Ready-made AI systems are easy to implement and adapt to common tasks, whereas custom AI agents are flexible, scalable, and can provide more long-term value to a particular business requirement.